5: The BµILD BUS
GP4020 GPS Baseband Processor Design Manual 31
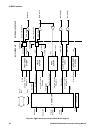
5 The BµILD BUS
The GP4020 Baseband Processor CPU subsystem is internally based around the BµILD bus. The ARM7TDMI
processor is connected to peripherals through its Bus for µController Integration in Low-Power Designs (BµILD).
Although the GP4020 user does NOT need to know details of the internal operation of the BµILD bus for most
applications, the implementation details are included for information.
This section contains a technical overview of the protocols associated with bus arbitration and bus transactions.
This represents sufficient information to give a working knowledge of the implementation of the BµILD Bus within
this embedded ARM system. The BµILD architecture is optimised for efficient on-chip embedded systems. It is
primarily designed to support ARM CPUs and support modules, but is extensible to other processors and logic.
The following text describes the essential aspects of BµILD including the principal functional elements and protocol
definitions.
5.1 Bus Masters
The bus master is the controller of the current bus transaction. A bus master initiates bus requests, generates
addresses and controls data transfers while it has bus access, by reading or writing data over the data bus.
Bus masters on the GP4020 are:
• The ARM7TDMI CPU
• Direct Memory Access (DMA) multi-channel controller(s)
• System Services Module (SSM) for external test and debug
5.2 Bus Slaves
A bus slave responds to addresses present on the internal Bus that are in its allocated range within the address
map. It supplies or receives data during read or write cycles on demand. A slave may set a wait signal to delay
access using the synchronous bus transfer protocol.