MAINTENANCE
2.12
5. Reverse the procedures to install the fuel valve.
6. Start engine and inspect for leaks.
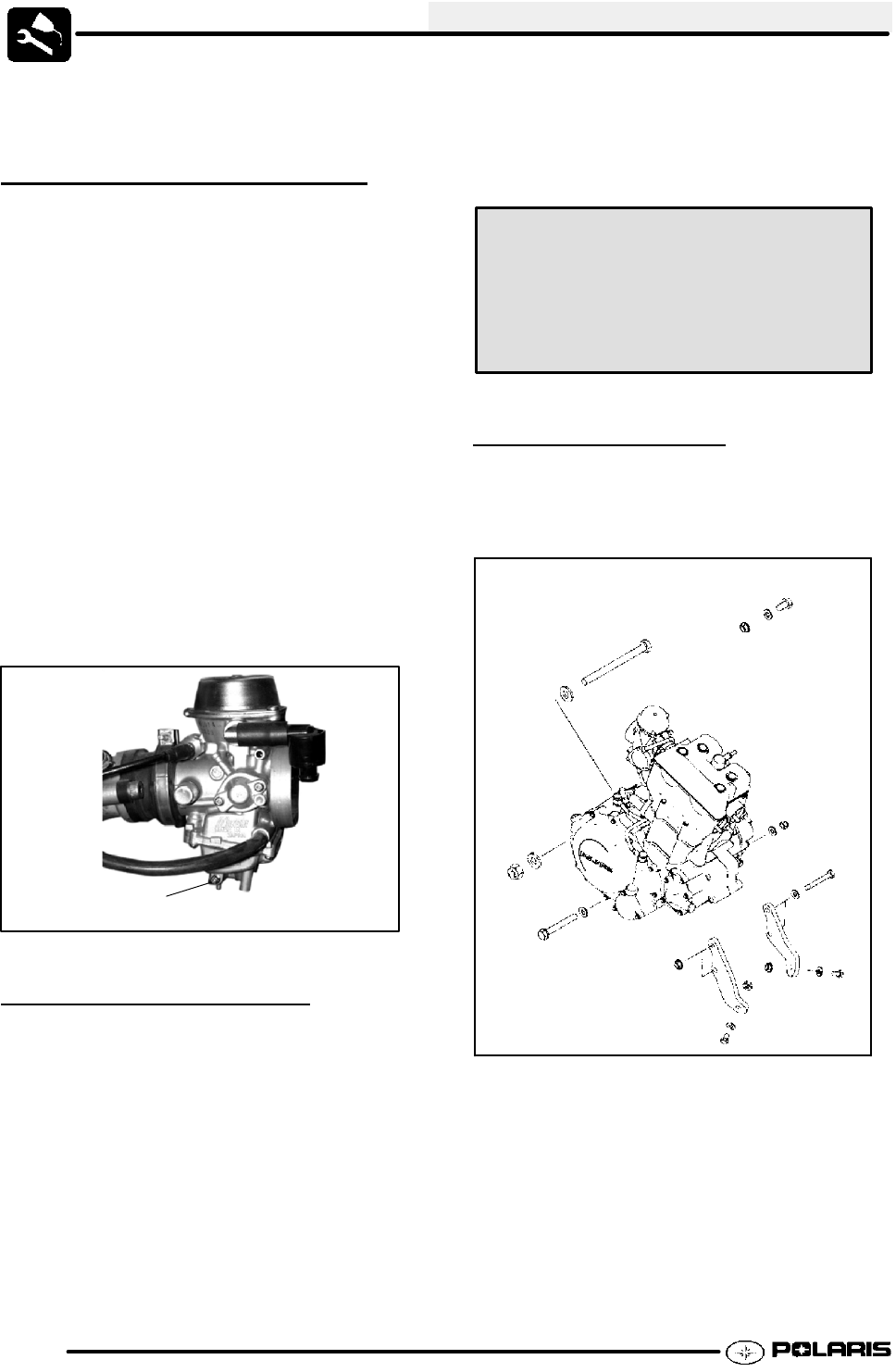
CARBURETOR DRAINING
The carburetor float bowl should be drained
periodically to remove moisture or sediment from the
bowl, or before extended periods of storage.
NOTE: The bowl drain screw is located on the bottom
left side of the float bowl.
1. Turn fuel valve to the off position.
2. Place a clean container beneath the bowl drain
spigot or bowl drain hose.
3. Turn drain screw out two turns and allow fuel in
the float bowl and fuel line to drain completely.
4. Inspect the drained fuel for water or sediment.
5. Tighten drain screw.
6. Turn fuel valve to “ON”.
7. Start machine and check for leaks.
NOTE: All tubes attached to the carburetor must be
check for pinching or blockage, as this will effect
engine performance.
Drain Screw
Ill. 1
COMPRESSION TEST
NOTE: This engine has built--in decompression
components. Compression readings will vary in
proportion to cranking speed during the test. Average
compression (measured) is about 85--90 psi @ 400
RPM during a compression test.
A smooth idle generally indicates good compression.
Low engine compression is rarely a factor in running
condition problems above idle speed. Abnormally
high compression can be caused by carbon deposits
in the combustion chamber or worn, damaged
exhaust cam lobes. Inspect camshaft and
combustion chamber if compression is abnormally
high.
A cylinder leakdown test is the best indication of
engine condition. Follow manufacturer’s instructions
to perform a cylinder leakage test. (Never use high
pressure leakage testers, as crankshaft seals may
dislodge and leak).
Cylinder Leakdown
Service Limit 10 %
(Inspect for cause if leakage exceeds 10%)
Cylinder Compression
w/ decompression
Standard: 85--90 PSI @ 400 RPM
ENGINE MOUNTS
Inspect engine mounts and frame for cracks or
damage. (Ill.3)
Check engine fasteners and ensure they are tight.
Ill. 3
Enfocus Software - Customer Support


















