5B.27
Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
5B
Electrical System
The EFI system is a 12 VDC negative ground system,
designed to operate down to a minimum of 7.0 volts. If
system voltage drops below this level, the operation of
voltage sensitive components such as the ECU, fuel
pump, and injectors will be intermittent or disrupted,
causing erratic operation or hard starting. A fully
charged, 12 volt battery with a minimum of 350 cold
cranking amps is important in maintaining steady and
reliable system operation. Battery condition and state of
charge should always be checked first when
troubleshooting an operational problem.
Keep in mind that EFI-related problems are more often
caused by the wiring harness or connections than by
the EFI components. Even small amounts of corrosion
or oxidation on the terminals can interfere with the
milliamp currents used in system operation. Cleaning
the connectors and grounds will solve problems in
many cases. In an emergency situation, simply
disconnecting and reconnecting the connectors may
clean up the contacts enough to restore operation, at
least temporarily.
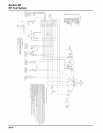
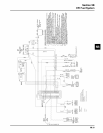
If a fault code indicates a problem with an electrical
component, disconnect the ECU connector and test
for continuity between the component connector
terminals and the corresponding terminals in the ECU
connector using an ohmmeter. Little or no resistance
should be measured, indicating that the wiring of that
particular circuit is OK. An illustrated listing of
numerical terminal locations, for each style of ECU/
connector is provided on pages 5B.28, 5B.31, or
5B.32.
5B.28 for “35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU
5B.31 for “24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU
5B.32 for “32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU
NOTE: When performing voltage or continuity tests,
avoid putting excessive pressure on or
against the connector pins. Flat pin probes
are recommended for testing to avoid
spreading or bending the terminals.