10.4
Section 10
Inspection and Reconditioning
The final cleaning operation should always be a
thorough scrubbing with a brush and hot, soapy water.
Use a strong detergent that is capable of breaking
down the machining oil while maintaining a good level
of suds. If the suds break down during cleaning,
discard the dirty water and start again with more hot
water and detergent. Following the scrubbing, rinse the
cylinder with very hot, clear water, dry it completely,
and apply a light coating of engine oil to prevent
rusting.
Measuring Piston-to-Bore Clearance
Before installing the piston into the cylinder bore, it is
necessary that the clearance be accurately checked.
This step is often overlooked, and if the clearances are
not within specifications, engine failure will usually
result.
NOTE: Do not use a feeler gauge to measure piston-
to-bore clearance – it will yield inaccurate
measurements. Always use a micrometer.
Use the following procedure to accurately measure the
piston-to-bore clearance:
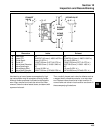
1. Use a micrometer and measure the diameter of
the piston 6 mm (0.24 in.) above the bottom of
the piston skirt and perpendicular to the piston
pin. See Figure 10-4.
3. Piston-to-bore clearance is the difference
between the bore diameter and the piston
diameter (step 2 minus step 1).
Flywheel
Inspection
Inspect the flywheel for cracks and the flywheel
keyway for damage. Replace the flywheel if it is
cracked. Replace the flywheel, the crankshaft, and the
key if flywheel key is sheared or the keyway is
damaged.
Inspect the ring gear for cracks or damage. Kohler
does not provide the ring gear as a serviceable part.
Replace the flywheel if the ring gear is damaged.
Cylinder Head and Valves
Inspection and Service
After cleaning, check the flatness of the cylinder head
and the corresponding top surface of the crankcase,
using a surface plate or piece of glass and feeler
gauge as shown in Figure 10-5. The maximum
allowable out of flatness is 0.076 mm (0.003 in.).
6 mm (0.24 in.)
Measure 6 mm above the
Bottom of Piston Skirt at
Right Angles to Piston Pin
Figure 10-4. Measuring Piston Diameter.
2. Use an inside micrometer, telescoping gauge, or
bore gauge and measure the cylinder bore. Take
the measurement approximately 63.5 mm
(2.5 in.) below the top of the bore and
perpendicular to the piston pin.
Figure 10-5. Checking Cylinder Head Flatness.
Carefully inspect the valve mechanism parts. Inspect
the valve springs and related hardware for excessive
wear or distortion. Check the valves and valve seat
area or inserts for evidence of deep pitting, cracks, or
distortion. Check clearance of the valve stems in the
guides. See Figure 10-6 for valve details and
specifications.