190-00592-06 Rev. A
Garmin G1000 Pilot’s Guide for the Diamond DA40/40F
17
SYSTEM OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
OVERVIEW
FLIGHT
INSTRUMENTS
EIS
AUDIO PANEL
& CNS
FLIGHT
MANAGEMENT
HAZARD
AVOIDANCE
AFCS
ADDITIONAL
FEATURES
APPENDICES INDEX
SATELLITE INFORMATION
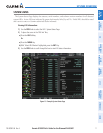
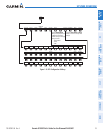
Satellites currently in view are shown at their respective positions on a satellite constellation diagram.
This sky view is always oriented north-up, with the outer circle representing the horizon, the inner circle
representing 45° above the horizon, and the center point showing the position directly overhead. Each satellite
is represented by an oval containing the Pseudo-random noise (PRN) number (i.e., satellite identification
number). Satellites whose signals are currently being used are represented by solid ovals.
The GPS Status Page can be helpful in troubleshooting weak (or missing) signal levels due to poor satellite
coverage or installation problems. As the GPS receiver locks onto satellites, a signal strength bar is displayed
for each satellite in view, with the appropriate satellite PRN number (01-32 or 120-138 for WAAS) below each
bar. The progress of satellite acquisition is indicated by signal bar appearance:
•Nosignalstrengthbar—Receiverislookingfortheindicatedsatellite.
•Hollowsignalstrengthbar—Receiverhasfoundthesatelliteandiscollectingdata.Eachsatellitehasa30-
second data transmission that must be collected (signal strength bar is hollow) before the satellite may be
used for navigation (signal strength bar becomes solid).
•Solidsignalstrengthbar—Receiverhascollectedthenecessarydataandthesatellitesignalcanbeused.
•Checkeredsignalstrengthbar—Receiverhasexcludedthesatellite(FaultDetectionandExclusion;FDE).
•“D”indicationonsignalstrengthbar—Satelliteisbeingusedfordifferentialcomputations.
•Greensignalstrengthbar—Satellitesthatareactuallybeingusedinthepositioncalculation.
•Bluesignalstrengthbar—Satelliteislockedonbutnotyetbeingusedinthepositioncalculation.
Using the current satellite signal information, they system calculates the aircraft’s GPS position, time,
altitude, ground speed, and track for the aircraft (displayed below the satellite signal accuracy measurements
for reference). The following quantities denote the accuracy of the aircraft’s GPS fix:
•EstimatedPositionUncertainty(EPU)—Astatisticalerrorindication;theradiusofacirclecenteredonan
estimated horizontal position in which actual position has 95% probability of lying
•HorizontalDilutionofPrecision(HDOP)—Measuressatellitegeometryquality(i.e.,numberofsatellites
received and where they are relative to each other) on a range from 0.0 to 9.9, with lower numbers denoting
better accuracy
•HorizontalandVerticalFiguresofMerit(HFOMandVFOM)—Measuresofhorizontalandverticalposition
uncertainty; the current 95% confidence horizontal and vertical accuracy values reported by the GPS
receiver