5B.16
Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
10. Remove the manifold mounting bolts and separate
the throttle body/manifold from the engine
leaving the TPS, fuel rail, air baffle, injectors and
line connections intact. Discard the old gaskets.
11. Position the manifold assembly over an
appropriate container and turn the key switch
“on” to activate the fuel pump and pressurize the
system. Do not turn switch to “start” position.
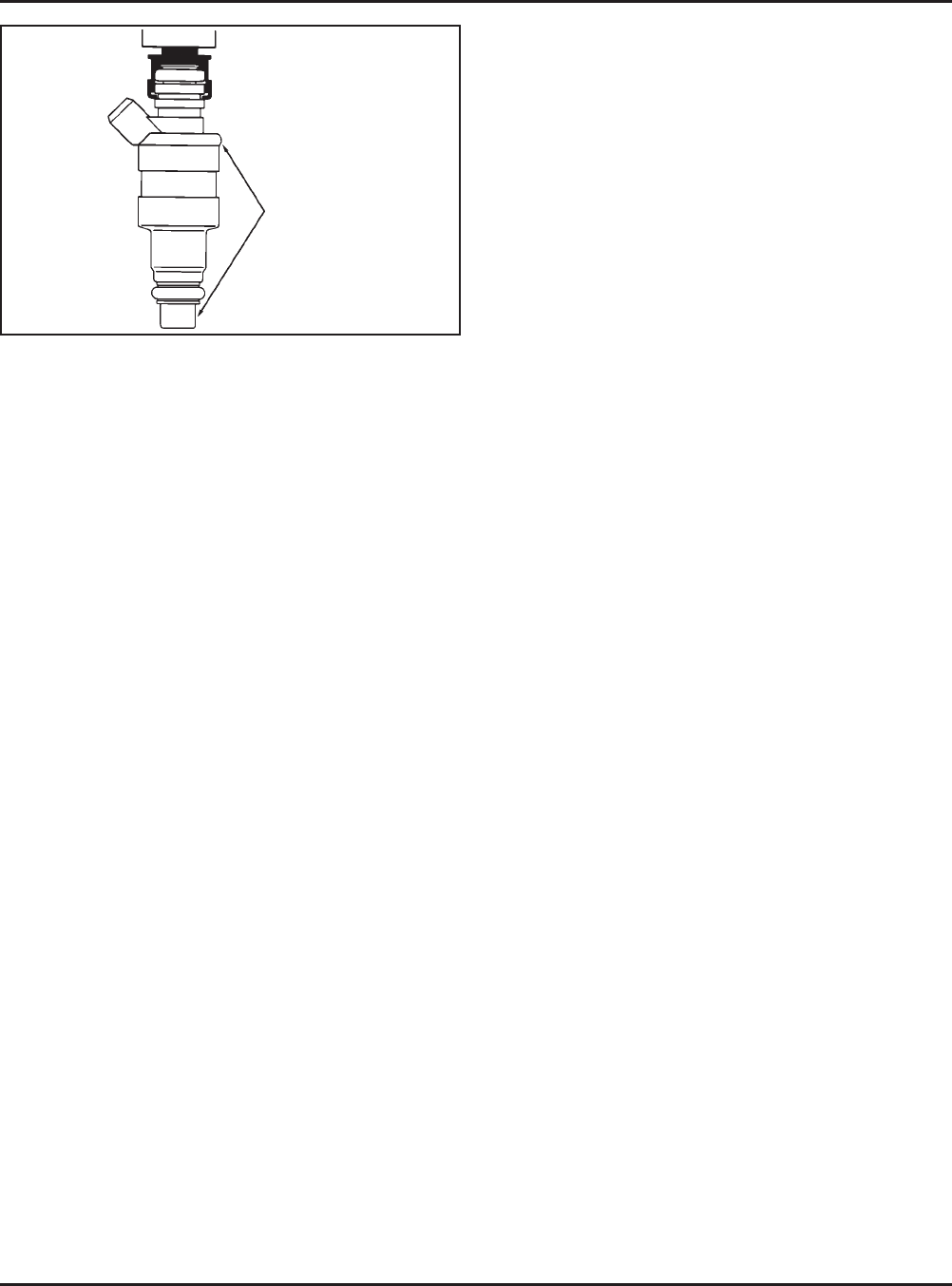
12. If either injector exhibits leakage of more than two
to four drops per minute from the tip, or shows
any sign of leakage around the outer shell, turn
the ignition switch off and replace the injector as
follows.
13. Depressurize the fuel system following the
procedure in the fuel warning on page 5B.2.
Remove the two fuel rail mounting screws.
14. Clean any dirt accumulation from the sealing/
mounting area of the faulty injector(s) and
disconnect the electrical connector(s).
15. Pull the retaining clip off the top of the injector(s).
Disconnect the fuel rail and remove the injector(s)
from the manifold.
16. Reverse the appropriate procedures to install the
new injector(s) and reassemble the engine. Use
new O-Rings any time an injector is removed (new
replacement injectors include new O-Rings).
Lubricate O-Rings lightly with oil. Torque the fuel
rail and blower housing mounting screws to
3.9 N·m (35 in. lb.), and the intake manifold and
air cleaner mounting screws to 9.9 N·m
(88 in. lb.).
Injector problems due to dirt or clogging are generally
unlikely due to the design of the injectors, the high fuel
pressure, and the detergent additives in the gasoline.
Symptoms that could be caused by dirty/clogged
injectors include rough idle, hesitation/stumble during
acceleration, or triggering of fault codes related to fuel
delivery. Injector clogging is usually caused by a
buildup of deposits on the director plate, restricting
the flow of fuel, resulting in a poor spray pattern.
Some contributing factors to injector clogging include
higher than normal operating temperatures, short
operating intervals, and dirty, incorrect, or poor quality
fuel. Cleaning of clogged injectors is not
recommended; they should be replaced. Additives and
higher grades of fuel can be used as a preventative
measure if clogging has been a problem.
Figure 5B-19. Injector Inspection Points.
1. Engine must be cool. Depressurize fuel system
through test valve in fuel rail.
2. Disconnect spark plug leads from spark plugs.
3. Remove the air cleaner outer cover, inner wing
nut, element cover and air cleaner element/
precleaner. Service air cleaner components as
required.
4. Remove the two screws securing the air cleaner
base to the throttle body manifold. Remove the
air cleaner base to permit access to the injectors.
Check condition of air cleaner base gasket,
replace if necessary.
5. Remove the flywheel screen if it overlaps the
blower housing.
6. If the engine has a radiator-type oil cooler
mounted to the blower housing, remove the two
oil cooler mounting screws.
7. Remove the blower housing mounting screws.
Note the location of the plated (silver) screw
attaching the rectifier/regulator ground lead.
Remove the blower housing.
8. Thoroughly clean the area around and including
the throttle body/manifold and the injectors.
9. Disconnect the throttle linkage and damper
spring from the throttle lever. Disconnect the TPS
lead from the harness.
Check For Leaks


















