5.30
Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
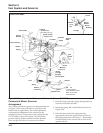
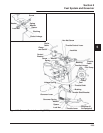
Figure 5-66. Governor Controls and Linkage
(External).
Initial Adjustment
NOTE: EFI engines require a special initial
adjustment procedure, which is covered in
subsection 5B. Refer to “Initial Governor
Adjustment” in that section for setting the
governor on EFI-equipped engines.
Procedure - Carburetor Equipped Engines
Make this adjustment whenever the governor arm is
loosened or removed from the cross shaft. See Figure
5-66 and adjust as follows:
1. Make sure the throttle linkage is connected to the
governor lever and the throttle lever on the
carburetor.
2. Loosen the hex nut holding the governor lever to
the cross shaft.
3. Move the governor lever toward the carburetor
as far as it will move (wide-open throttle) and
hold in position.
4. Insert a nail into the hole in the end of the cross
shaft and rotate the shaft counterclockwise as far
as it will turn, then tighten the hex nut securely.
Adjustments
General
The governed speed setting is determined by the
position of the throttle control. It can be variable or
constant, depending on the engine application.
Governor
General
The engine is equipped with a centrifugal flyweight
mechanical governor. It is designed to hold the engine
speed constant under changing load conditions. The
governor gear/flyweight mechanism is mounted
inside the crankcase on the oil pan, and is driven off
the gear on the camshaft. The governor works as
follows:
• Centrifugal force acting on the rotating governor
gear assembly causes the flyweights to move
outward as speed increases. Governor spring
tension moves them inward as speed decreases.
• As the flyweights move outward, they cause the
regulating pin to move outward.
• The regulating pin contacts the tab on the cross
shaft causing the shaft to rotate. One end of the
cross shaft protrudes through the crankcase. The
rotating action of the cross shaft is transmitted to
the throttle lever of the carburetor through the
external linkage. See Figure 5-66.
• When the engine is at rest, and the throttle is in
the “fast” position, the tension of the governor
spring holds the throttle plate open. When the
engine is operating, the governor gear assembly
is rotating. The force applied by the regulating
pin against the cross shaft tends to close the
throttle plate. The governor spring tension and
the force applied by the regulating pin balance
each other during operation, to maintain engine
speed.
• When load is applied and the engine speed and
governor gear speed decreases, the governor
spring tension moves the governor lever to open
the throttle plate wider. This allows more fuel
into the engine, increasing engine speed. As
speed reaches the governed setting, the governor
spring tension and the force applied by the
regulating pin will again offset each other to hold
a steady engine speed.
Hex
Nut
Cross Shaft
Governor Spring
Governor
Arm