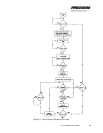
3.7 Monitoring System Health
The firmware program continuously monitors system health while the
HFG2.0 is powered. If any of the health parameters are out of the normal
operating range, the MCE outputs a discrete fault alarm to the user’s
controller.
Some fault causes are:
• MCE over-current
• Tracking error
• RDC failure
• Input voltage out of range
Fault Alarms
The HFG2.0 features two discrete, non-latching outputs that are
configured as fault alarms. Upon power-up, the fault circuits close and
stay closed in the normal operating condition. When the HFG2.0 detects
a system fault, it opens the fault circuit designated for that particular fault.
If a fault alarm is detected, the user should shut down the HFG2.0 to
investigate the failure cause. Removing 120 VDC power shuts down the
HFG2.0 valve.
Toggling the RESET command will clear the alarms.
FAULT Alarm
The configuration of faults assigned to the FAULT alarm is programmable
in the most recent generation
of the HFG2.0 (factory-configurable
only). See Table 3-1 for the default configuration
of faults assigned to
the FAULT alarm.
See Table 3-3 for a list of fault conditions represented by the FAULT
alarm in earlier generations
of the HFG2.0.
OVERTEMP Alarm
The configuration of faults assigned to the OVERTEMP alarm is
programmable in the most recent generation
of the HFG2.0 (factory-
configurable only). In the default configuration, the Motor Over Temp fault
is the only fault assigned to the OVERTEMP alarm. If the HFG2.0 detects
that the temperature in two or more of the motor windings is 135° C or
higher, the OVERTEMP alarm circuit opens. See Table 3-2 for details
about the default configuration
of the OVERTEMP alarm.
CH. 3: OPERATING THE HFG2.0 45