A–10
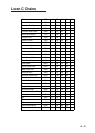
Glossary
Almanac
Each GPS satellite broadcasts its own orbital
data as well as general orbital data of all other
GPS satellites. This general orbital data is
called the Almanac. The GPS receiver
receives the Almanac and decodes it to
calculate the quantity and elevation angle of
satellites in view, to know when it can receive
the GPS signal. If there is no Almanac in the
receiver it cannot fix its position. The receiver
is shipped with no Almanac, thus when it is
turned on for the first time it starts receiving
the Almanac. Each time the unit is turned on
the previous Almanac is erased and the latest
received.
Beacon receiver
The DGPS (Differential GPS) station
transmits a beacon signal which contains
information about GPS error. The device
which receives the beacon signal is called a
beacon receiver.
Cold start
When the GPS receiver is turned on for the
very first time, it starts receiving the Almanac.
This condition is called cold start. In this
condition it takes about two minutes to find
position. Once the Almanac is stored in the
GPS navigator, it takes only about 20 seconds
to find position. (The normal start-up
condition is called warm start.)
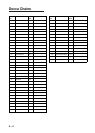
Destination
A destination can be either a single destination
waypoint or a series of waypoints leading to
the ultimate destination. When you set a
destination, the GPS receiver provides range
and bearing data to the destination, to help
you steer to the destination along the shortest
past possible.
Differential GPS (DGPS)
The differential GPS system, consisting of
DGPS land stations and DPGS beacon
receiver-equipped marine vessels, further
refines the accuracy of the GPS measured
position.
A DGPS land station knows its exact position.
If there is a difference between GPS position
and DGPS land station's position this is called
GPS error. The DPGS station transmits GPS
error data to a beacon receiver which relays
the data to the GPS receiver. The GPS receiver
uses this data to refine the accuracy of the GPS
position (within about 10 meters under ideal
conditions).
DGPS stations are strategically located
throughout America (including Hawaii and
Alaska), Europe, Canada, Bermuda and
Brazil.
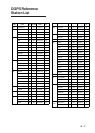
Estimated time of arrival (ETA)
The time at which you arrive at the ultimate
destination.
Geodetic chart
A nautical chart is usually made by either
trigonometrical survey or astronomical survey
and according to the geodetic chart standards
of the country where it is used. The GPS
standard chart system is WGS-84.
Thus if you are using a chart different from
WGS-84, there will be error between GPS
position and nautical chart position. To get
correct position, the GPS receiver must know
what chart system you are using, to apply an
offset to GPS position.
GPS measured position
GPS measured latitude and longitude position.
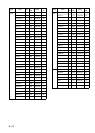
Intermediate waypoint
A waypoint in a route.