10–2
10.3 What is Differential GPS
(DGPS)?
Differential GPS is based upon accurate
knowledge of the accurate geograhical loca-
tion of a reference station which is used to
compute corrections to GPS parameters, er-
ror sources and resultant positions. These dif-
ferential corrections are transmitted to GPS
users, who apply the corrections to their re-
ceived GPS signals or computed position. For
civil users, differential corrections can im-
prove navigational accuracy from 100 meters
to better than 3 meters.
The DPGS reference stations, located through-
out North America and Europe, are fixed at a
geodetically surveyed position. The reference
station tracks all satellites in view, downloads
ephemeric data from them, and computes cor-
rections based on its measurement and geo-
detic position. These corrections are then
broadcast to GPS users by radio beacons to
improve their position solution.
The radio beacons broadcast in the frequency
range of 285–325 kHz and have a transmit-
ting range from 40 nm to 300 nm depending
on radio beacon.
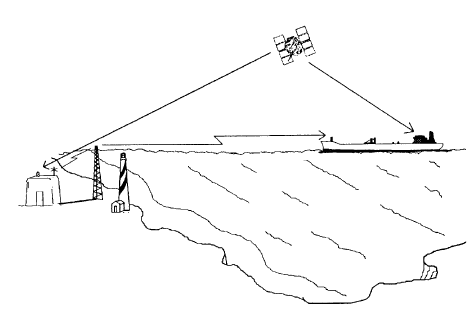
Corrections sent
to users
GPS
satellite
Reference
station
Figure 10-3 DGPS system concept