5-2 Troubleshooting MN894
SCR Tests If the SCR devices are suspected of failure, these tests can be used to test the SCR’s.
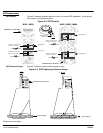
Inspection Be sure the physical condition of components is correct. Refer to Figure 5-1.
1. Be sure power is off.
2. Inspect power cell connections for tightness and signs of overheating.
3. Replace snubber capacitors if there is any sign of oil or fluid leaking.
Snubbers are not used on size 55 and 80 amp power cells.
4. Inspect SCR clamp insulator for cracks.
5. SCR clamps should be tightened evenly.
(Use clamp gauge available from Baldor).
6. Inspection and resistance test should be performed when system has
experienced:
Logic Control Module failure
MOV failure
Starting or running current imbalance
SCR replacement
Phase loss or single phasing
7. Heat sinks and insulating surfaces must be clean and unobstructed.
8. Size 55 and 80 amp power cells do not have snubber networks, SCR clamps or
insulating base.
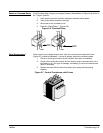
Full Voltage Test After the motor reaches rated speed and the control is no longer in current limit, the
SCR’s turn full on and deliver full voltage to the motor. When power factor correction
(PF) is used, the control will reduce the voltage to the motor. For this reason, the PF
adjustment should be set to “OFF” during this test. Refer to Figure 5-1.
1. Set the PF adjustment should be set fully CW (OFF) during this test.
2. Turn power on. Wait for the motor to reach full speed.
3. With the control in the run mode, measure the voltage across the line side to
the load side on each control power cell or SCR pack. The voltage should be
about 2 to 20 VAC. The voltage reading will vary depending upon the motor
and the type of meter used. Voltage readings must be balanced on all three
phases.
4. If the voltage is higher across one or two power cells or SCR packs, not all
SCR’s are firing properly.
5. If all three cells or SCR packs have approximately the same voltage drop
across line to load when the motor is up to speed and motor current is
unbalanced, the cause is the motor or unbalanced line voltage.