Section 3
Operation
Operation 3-1MN894
Types of Starting
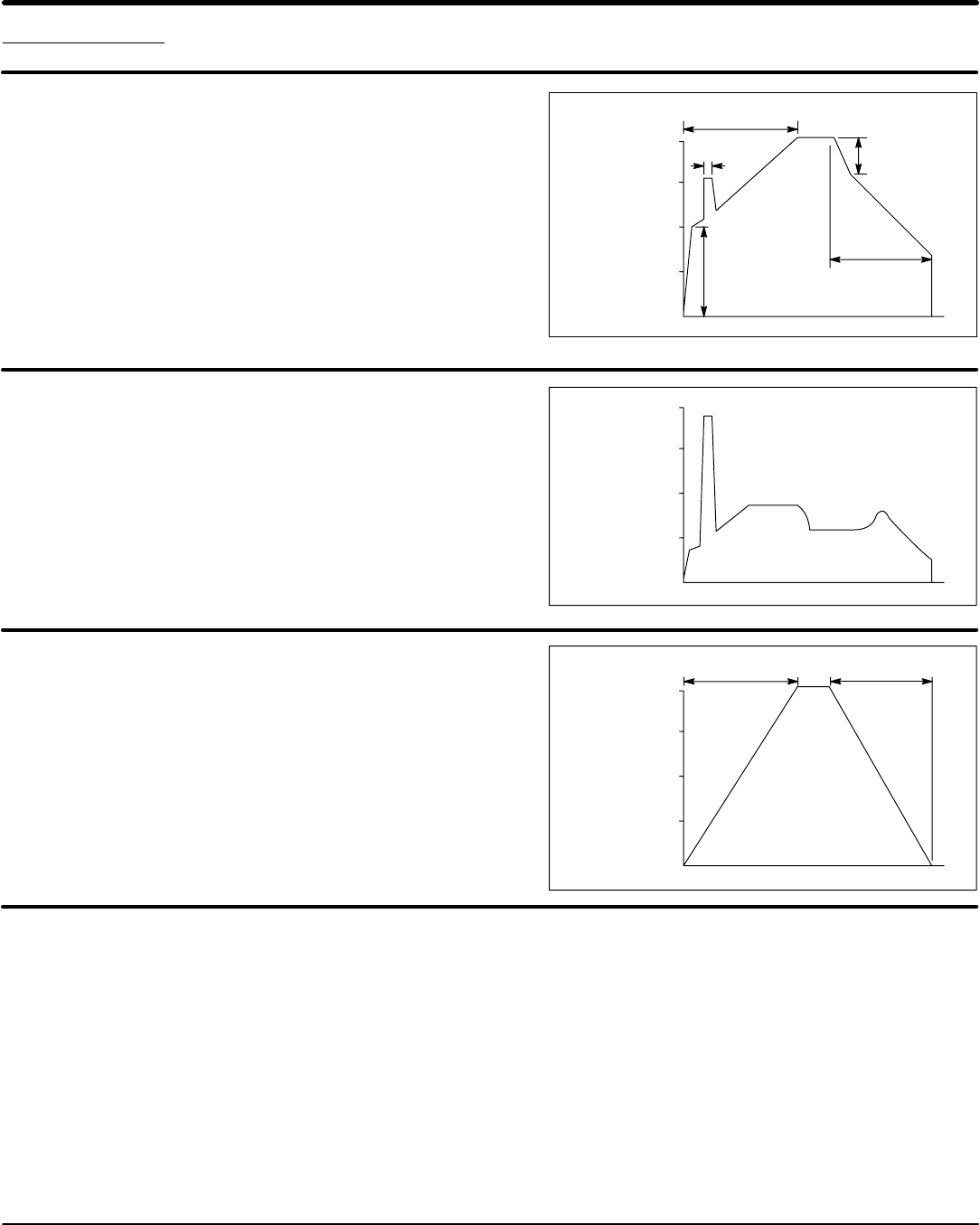
Voltage
Ramp
% Line
Voltage
25
50
75
100
RU
TD
CL
RD
TU
Time
0
PT
Current
Limit
% FLA
100
200
300
400
CL
RD
Time
0
PT
Tach
% Full
Speed
25
50
75
100
RU
RUN
RD
Time
0
Voltage Starting (S2-4 = OFF)
During start the initial voltage (TU) is set to a level where the
motor will begin to turn when power is applied. The ramp time
(RU) is adjustable to provide a smooth start. The pulse time
(PT) is used for high friction loads to break loose “frozen” loads
with up to 400% FLA.
If a ramp down function is needed, the initial voltage TD setting
is used to lower voltage to a level where the motor will begin to
slow down when the stop button is pushed. Ramp down (RD)
can only extend motor stopping time preventing sudden stopping
problems such as water hammer.
Current Limit Starting (S2-5 = ON)
If current limit starting is selected the starter will operate similar
to voltage starting. On high inertia loads such as chippers and
grinders the Current Limit (CL) setting is what determines the
starting time. The starter will provide that current regardless of
the ramp time setting. The CL setting must be high enough to
provide enough starting current in all starting conditions. Ramp
down (RD) can only extend motor stopping time preventing
sudden stopping problems such as water hammer.
Tach Feedback Starting (S2-4 = ON)
Tach feedback starting/stopping uses a 0-10 VDC Tach signal.
The control will provide voltage to the motor to generate a
smooth linear starting even under cycling load conditions. Ramp
down (RD) can only extend motor stopping time preventing
sudden stopping problems such as water hammer.