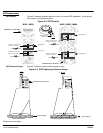
Start-up 4-7MN894
Tachometer Mode (S2-4=ON, S2-5=OFF)
Typically used for changing loads that require consistent starting and stopping times,
independent of load condition, and pumping applications with severe head pressure to
reduce water hammer; i.e., pumps, conveyors, stackers and other material handling
equipment.
1. Set RU, TU, PT, RD, TD and PF fully counterclockwise (CCW).
2. Set CL and CM fully clockwise (CW).
3. Adjust RU and RD for desired ramp up and ramp down time. RD is only
effective with S2-1=OFF.
Running Adjustment Procedure:
After adjusting the starting and stopping characteristics, the current monitor/trip (CM)
and power factor correction circuit (PF) can be adjusted. If the power factor circuit is
not used, turn the PF adjustment fully counterclockwise.
Power Factor Correction Adjustment (PF):
1. Use an ammeter to measure motor running current.
2. With the motor at full speed, minimum load and SSC “Ramp End” light ON,
adjust PF clockwise to minimize running current without oscillation. If there is
no noticeable drop in current, repeat this step while measuring motor voltage.
Current Monitor/Trip (CM):
1. Set S2-2=OFF.
2. Press start and allow motor to reach full speed and the “Ramp End” light to turn
ON.
3. Adjust CM to the desired threshold by observing the “CUR MON” light.
4. The “CUR MON” contact can be used to signal this threshold, or by setting the
S2-2=ON, the starter will shut down. Press stop to reset the shutdown and trip
condition.
Post Adjustment Check List:
1. Check fans for proper operation
2. If a bypass contactor is used, check to ensure that the contactor closes at ramp
end.
3. Using a current probe, measure current on all three motor phases. Be sure the
current is balanced during ramp up, run and ramp down.
4. With the motor in run mode (ramp end light “ON”), check phase current of all
three phases. Currents should be balanced and within nameplate FLA.
5. Measure the line voltage at the control during ramp up to ensure voltage does
not drop below minimum operating voltage.