3.11
ENGINE
3
3. If the crank rod pin location is 180
o
from the dial indicator
(opposite that shown above), it will be necessary to spread
the crankshaft at position A as shown in the illustration at
right. When rebuilding and straightening a crankshaft,
runout must be as close to zero as possible.
NOTE: Maximum allowable runout is .0024”.
Engine Lubrication-
EH 50PL
Oil Type:Polaris Premium 4 Synthetic
(PN 2871281); or API certified “SH” 0-40W oil
Capacity:. . . . . . . .Approximately 2 U.S. Quarts (1.9 l)
Filter Wrench . . . .(PV-43527)
*Drain Plug / Screen Fitting...14 ft. lbs. (19 Nm) (If fitting is
removed, follow oil pump priming procedure).
*Oil Pressure Specification...20 PSI @ 5500 RPM, Polaris
0W-40 Synthetic (Engine Hot)
Oil Pressure Test - EH 50PL
1. Remove blind plug on front left cylinder head.
2. Insert a 1/8 NPT oil pressure gauge adaptor into the cylinder
head and attach the gauge.
3. Start engine and allow it to reach operating temperature,
monitoring gauge indicator.
NOTE: Use only Polaris Premium 4 Synthetic Engine
Lubricant (PN 2871281).
Oil Pump Priming Procedure
See “Oil Pump Priming Procedure” on page 2.25.
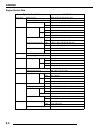
Oil Flow - EH50PL
The following chart describes the flow of oil through the
EH50PL engine. Beginning at the oil tank, the oil flows through
a screen fitting in the bottom of the tank and into the oil supply
hose. The feed side of the oil pump draws oil through the hose
and into the crankcase oil gallery, and then pumps the oil
through another passage to the one way valve. (When the engine
is off, the one way valve closes to prevent oil in the tank from
draining into the crankcase.) The oil is pumped through a
delivery pipe to the oil filter. If the oil filter is obstructed, a
bypass valve contained in the filter allows oil to bypass the filter
element.
At this point, the oil is diverted in two directions. Oil is supplied
to the camshaft through the left front cylinder stud, and an oil
passage in the head. Oil enters the camshaft through the PTO (L)
journal. The camshaft journals, cam lobes, and rocker arms are
lubricated through holes in the camshaft. The oil lubricates the
cam chain and sprocket and drains to the sump.
The other oil path from the filter leads through a delivery pipe
to the crankcase main oil gallery, which leads to the stator plate
oil passage. Here it passes through the slotted friction bearing
(located in the stator plate) into the crankshaft. An oil seal on the
stator plate prevents oil from entering the stator/flywheel area.
Oil travels through the crankshaft to the crank pin, lubricating
the connecting rod large end bearing directly. Oil also passes
through an oil jet (drilled orifice) in the end of the crank pin to
the PTO end main bearings and counterbalancer gears.
Residual oil from the lubrication of the crankshaft and
connecting rod indirectly lubricates the cylinder wall, piston,
rings, connecting rod small end bearing, piston pin, oil/water
pump drive gears, cam chain and drive sprocket, and Magneto
end crankshaft main bearing.
The one-way valve is located on the front left (PTO) side of the
crankcase. The valve prevents oil in the tank from draining into
the engine sump when the engine is off. The valve mechanism
consists of a plunger, return spring, guide plug, and sealing
washer. When the engine is running, oil pressure lifts the
plunger off the seat, allowing oil flow. When the engine is off,
spring pressure forces the plunger against the oil passage seat,
preventing oil flow from the tank to the sump. The one-way
valve requires very little maintenance. If engine oil drains into
the sump when the engine is off, inspect the valve sealing
surface for debris or damage. Inspect the return spring for
distortion or damage.
Oil Pressure at 5500 RPM (Engine Hot):
Standard: 20 PSI
Minimum: 12 PSI