Appendix B Command Syntax and Style
Command Types, Format, and Elements
Operating and Programming Guide B-11
XYZ ASCII-encoded bytes corresponding to the literal used as the command
parameter.
An example of an alphanumeric response is: NONE
“XYZ ” A string response consists of ASCII characters enclosed by double quotes.
For example, string data is used for the “<error description>” portion of
:SYST:ERR? response.
“XYZ”, ... A list of string responses consist of comma-separated ASCII characters
enclosed by double quotes.
(e.g., “log 224:19951017.00:00:26:30: Holdover started, GPS”,
“log 225:19951017.00:00:29:02: GPS lock started”)
ASCII Data A sequence of ASCII-encoded bytes.
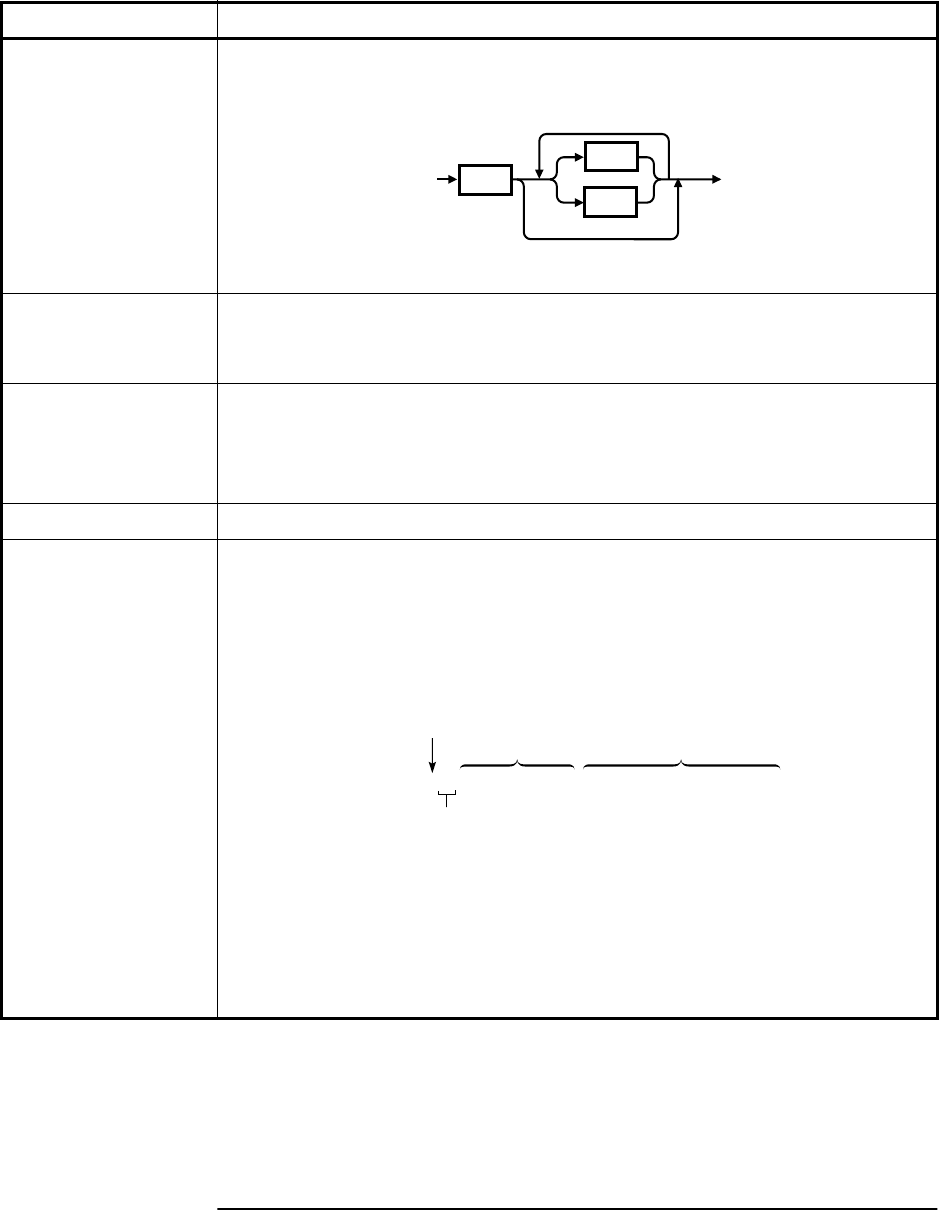
Binary Data The syntax is a pound sign (#) followed by a non-zero digit representing the
number of digits in the subsequent decimal integer. The decimal integer
specifies the number of 8-bit data bytes being sent. This is followed by the
actual data. The terminator is a line feed. For example, for transmitting 8 bytes
of data, the format might be:
The “2” indicates the number of digits that follow and the two digits “08” indicate
the number of data bytes to be transmitted.
<carriage return> is defined as a single ASCII-encoded byte corresponding to
13 decimal.
<new line> is defined as a single ASCII-encoded byte corresponding to
10 decimal.
Table B-3. Response Formats (Continued)
Format Description
alpha
digit
alpha
<carriage return><8 bytes of data>2#08
TerminatorActual data
Number of digits
that follow
Number of bytes
to be transmitted
<new line>