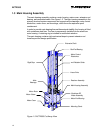
ACT2000
1.7 Linear Drive Mechanism
The Linear Drive Mechanism converts the rotary motion of the Motor Assembly to
linear actuator motion. The core of the mechanical drive system is the linear ball
screw drive containing a screw shaft, ball bearing fitted nut, extension rod and
main duplex thrust bearings.
Screw Shaft
The thrust bearings, motor rotor, motor end bearing, and resolver rotor are
mounted directly to the screw shaft. A ball bearing track is machined into the
screw shaft.
Ball Nut
As the screw shaft rotates, the ball nut translates in an axial direction depending
on shaft rotation.
Extension Rod and Bearings
The extension rod is threaded on the ball nut. As the ball nut translates, the
extension rod moves in and out of the ACT2000 main housing.
The extension rod support bearing is provided for lateral support. Thrust and
radial loads are transferred from the extension rod through the ball nut to the main
preloaded duplex thrust bearings. The thrust bearings transfer the loads to the
main housing by the main bearing and shaft retaining nuts.
A motor end bearing is provided for additional shaft radial stability. The resolver
rotor, motor rotor, motor bearing, and spacers are stacked on the ball screw shaft
and retained by a single nut. This arrangement prevents actuator axial loads from
passing through the resolver rotor and motor rotor.
1.8 Power and Digital Harness
A four-wire electrical harness with two (2) meter free leads provides the ACT2000
electrical power inputs. The four-wire harness allows for redundant electrical
inputs.
A seventeen-wire electrical harness with ninety (90) inch free leads provides
ACT2000 signal interface. Contained within this seventeen-wire harness are
discrete commands, analog commands, feedback, and serial interface wires.
1-4