TRAILER MAINTENANCE
This section is intended to provide the user with generic
trailer service and maintenance information. The service
and maintenance guidelines referenced in this section refer
to a wide range of trailers.
Remember periodic inspection of the trailer will ensure safe
towing of the generator and will prevent personal injury and
damage to the equipment.
The definitions below describe some of the major
components of a typical trailer that would be used with
generator.
1. Fuel Cell — Provides an adequate amount of fuel for
the equipment in use. Fuel cells must be empty when
transporting equipment.
2. — System employed in stopping
the trailer. Typical braking systems are electric, surge,
hydraulic, hydraulic-surge and air.
3. — Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) is
the maximum number of pounds the trailer can carry,
including the fuel cell (empty).
4. — Measurement is from the ball hitch
to the rear bumper (reflector).
5. Frame Width — Measurement is from fender to
fender
6. Jack Stand — Trailer support device with maximum
pound requirement from the tongue of the trailer.
7. Coupler — Type of hitch used on the trailer for
towing.
8. Tire Size — Indicates the diameter of the tire in
inches (10,12,14, etc.), and the width in millimeters
(175,185,205, etc.). The tire diameter must match the
diameter of the tire rim.
9. Tire Ply — The tire ply (layers) number is rated in
letters; 2-ply,4-ply,6-ply, etc.
10. Wheel Hub — The wheel hub is connected to the
trailer’s axle.
11. Tire Rim — Tires mounted on a tire rim. The tire rim
must match the size of the tire.
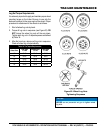
12. — Used to secure the wheel to the wheel
hub. Always use a torque wrench to tighten down
the lug nuts. See Table 18 and Figure 62 for lug nut
tightening and sequence.
13. Axle — Indicates the maximum weight the axle can
support in pounds, and the diameter of the axle
expressed in inches. Please note that some trailers
have a double axle. This will be shown as 2-6000 lbs.,
meaning two axles with a total weight capacity of 6000
pounds.
14. Suspension — Protects the trailer chassis from shocks
transmitted through the wheels. Types of suspension
used are leaf, Q-flex, and air ride.
15. Electrical — Electrical connectors (looms) are provided
with the trailer so the brake lights and turn signals can
be connected to the towing vehicle.
16. Application — Indicates which units can be employed
on a particular trailer.