MOT Test Checks REF•3
REF
Exhaust system
Ⅺ Start the engine. With your assistant
holding a rag over the tailpipe, check the
entire system for leaks. Repair or renew
leaking sections.
Jack up the front and rear of the vehicle,
and securely support it on axle stands.
Position the stands clear of the suspension
assemblies. Ensure that the wheels are
clear of the ground and that the steering
can be turned from lock to lock.
Steering mechanism
Ⅺ Have your assistant turn the steering from
lock to lock. Check that the steering turns
smoothly, and that no part of the steering
mechanism, including a wheel or tyre, fouls
any brake hose or pipe or any part of the body
structure.
Ⅺ Examine the steering rack rubber gaiters
for damage or insecurity of the retaining clips.
If power steering is fitted, check for signs of
damage or leakage of the fluid hoses, pipes or
connections. Also check for excessive
stiffness or binding of the steering, a missing
split pin or locking device, or severe corrosion
of the body structure within 30 cm of any
steering component attachment point.
Front and rear suspension and
wheel bearings
Ⅺ Starting at the front right-hand side, grasp
the roadwheel at the 3 o’clock and 9 o’clock
positions and shake it vigorously. Check for
free play or insecurity at the wheel bearings,
suspension balljoints, or suspension mount-
ings, pivots and attachments.
Ⅺ Now grasp the wheel at the 12 o’clock and
6 o’clock positions and repeat the previous
inspection. Spin the wheel, and check for
roughness or tightness of the front wheel
bearing.
Ⅺ If excess free play is suspected at a
component pivot point, this can be confirmed
by using a large screwdriver or similar tool and
levering between the mounting and the
component attachment. This will confirm
whether the wear is in the pivot bush, its
retaining bolt, or in the mounting itself (the bolt
holes can often become elongated).
Ⅺ Carry out all the above checks at the other
front wheel, and then at both rear wheels.
Springs and shock absorbers
Ⅺ Examine the suspension struts (when
applicable) for serious fluid leakage, corrosion,
or damage to the casing. Also check the
security of the mounting points.
Ⅺ If coil springs are fitted, check that the
spring ends locate in their seats, and that the
spring is not corroded, cracked or broken.
Ⅺ If leaf springs are fitted, check that all
leaves are intact, that the axle is securely
attached to each spring, and that there is no
deterioration of the spring eye mountings,
bushes, and shackles.
Ⅺ The same general checks apply to vehicles
fitted with other suspension types, such as
torsion bars, hydraulic displacer units, etc.
Ensure that all mountings and attachments are
secure, that there are no signs of excessive
wear, corrosion or damage, and (on hydraulic
types) that there are no fluid leaks or damaged
pipes.
Ⅺ Inspect the shock absorbers for signs of
serious fluid leakage. Check for wear of the
mounting bushes or attachments, or damage
to the body of the unit.
Driveshafts
(fwd vehicles only)
Ⅺ Rotate each front wheel in turn and inspect
the constant velocity joint gaiters for splits or
damage. Also check that each driveshaft is
straight and undamaged.
Braking system
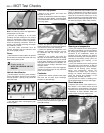
Ⅺ If possible without dismantling, check
brake pad wear and disc condition. Ensure
that the friction lining material has not worn
excessively, (A) and that the discs are not
fractured, pitted, scored or badly worn (B).
Ⅺ Examine all the rigid brake pipes
underneath the vehicle, and the flexible
hose(s) at the rear. Look for corrosion, chafing
or insecurity of the pipes, and for signs of
bulging under pressure, chafing, splits or
deterioration of the flexible hoses.
Ⅺ Look for signs of fluid leaks at the brake
calipers or on the brake backplates. Repair or
renew leaking components.
Ⅺ Slowly spin each wheel, while your
assistant depresses and releases the
footbrake. Ensure that each brake is operating
and does not bind when the pedal is released.
3 Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE RAISED
AND THE WHEELS FREE TO
TURN