CAUTION (Continued)
• Underinflated tires pose
the same danger as
overloaded tires. The
resulting accident could
cause serious injury.
Check all tires frequently to
maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure
should be checked when
your vehicle’s tires are
cold. See Inflation - Tire
Pressure on page 5-43.
• Overinflated tires are more
likely to be cut, punctured,
or broken by a sudden
impact — such as when
you hit a pothole. Keep
tires at the recommended
pressure.
• Worn, old tires can cause
accidents. If the tire’s tread
is badly worn, or if your
vehicle’s tires have been
damaged, replace them.
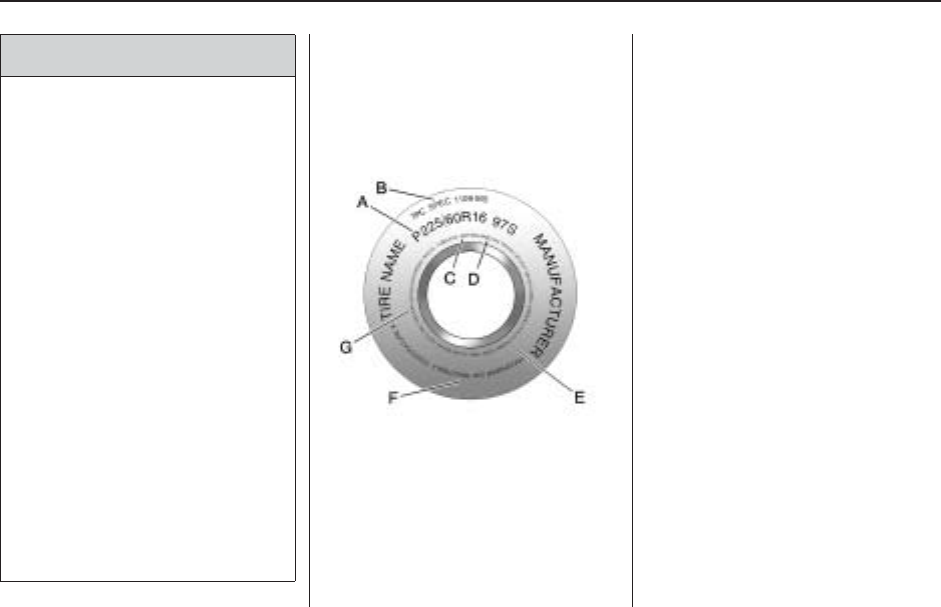
Tire Sidewall Labeling
Useful information about a tire is
molded into its sidewall. The
example below shows a typical
passenger (p-metric) tire
sidewall.
(A) Tire Size
: The tire size is a
combination of letters and
numbers used to define a
particular tire’s width, height,
aspect ratio, construction
type, and service description.
See the “Tire Size” illustration
later in this section for more
detail.
(B) TPC Spec (Tire
Performance Criteria
Specification)
: Original
equipment tires designed to
GM’s specific tire performance
criteria have a TPC specification
code molded onto the sidewall.
GM’s TPC specifications meet or
exceed all federal safety
guidelines.
(C) DOT (Department of
Transportation)
: The
Department of Transportation
(DOT) code indicates that the tire
is in compliance with the U.S.
Department of Transportation
Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
(D) Tire Identification Number
(TIN)
: The letters and numbers
following DOT code are the
Tire Identification Number (TIN).
The TIN shows the manufacturer
and plant code, tire size, and
date the tire was manufactured.
Passenger (P-Metric) Tire
Example
Service and Appearance Care 5-39