9
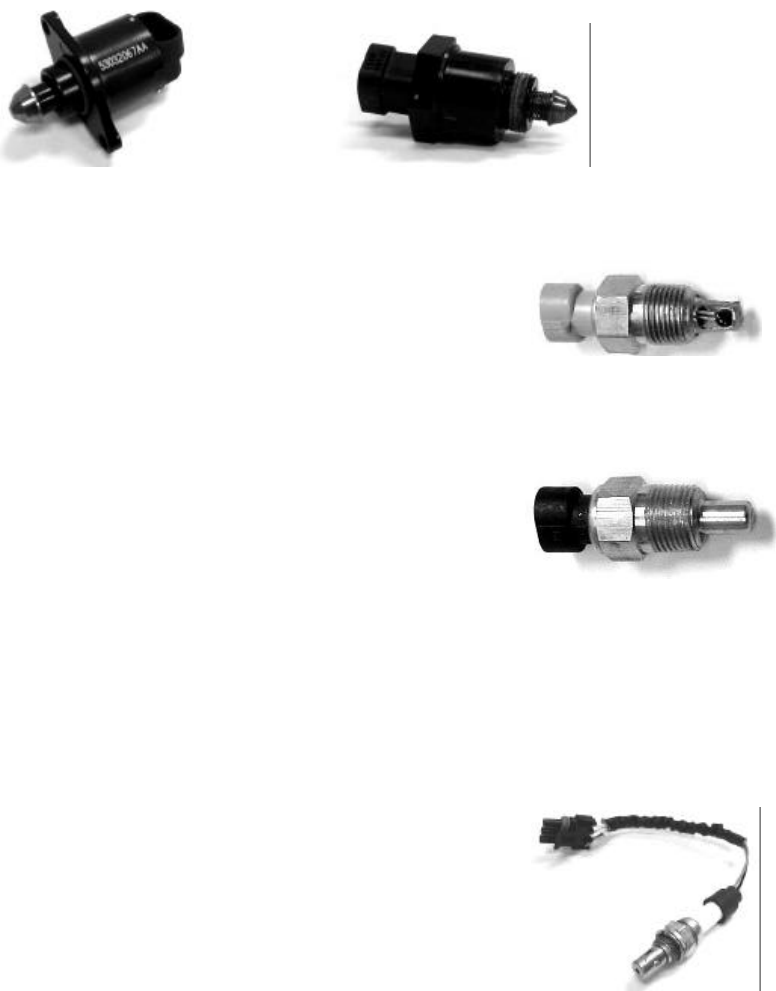
1.9 Idle Air Control Valve (IAC)
The IAC is located in the throttle body of the TBI and MPFI. The valve consists of a stepper motor that adjusts the position of
its pintle to vary the bypass air during idle and of idle conditions. During the closed throttle condition (idle), the ECU constantly
compares actual engine speed with the programmed desired engine speeds. Discrepancy between these two values result in
activation of the stepper motor increasing or decreasing the bypass air around the throttle plates until desired engine speed is
achieved. This operation is similar to a controlled vacuum leak. The following input signals or conditions determine the
position of the valve:
• Throttle position sensor
• Engine load (MAP, A/C compressor, power steering, gear selection)
• Engine coolant temperature
Bolt-In IAC Screw-In IAC
1.10 Manifold Air Temperature Sensor
The air charge sensor is located in the engine air intake to sense the air induced into the
engine manifold. The sensor consists of a thermistor, which generates a voltage signal, that
is proportional to the air temperature. This voltage signal is used by the ECU to calculate
the air density and using these results to adjust the fueling levels for a particular engine
load. A function of the air temperature signal is to:
Manifold Air Temperature Sensor
• Adjust fueling during cold start based on air temperature
1.11 Coolant Temperature Sensor
The coolant temperature sensor is a two-wire sensor that is threaded into the engine block
and is in direct contact with the coolant. The function of this sensor is to generate a signal
that the ECU uses to adjust the fueling levels required for the operation of the engine and
operate ancillaries. The thermistor contained in the sensor generates an electric signal
that is proportional to the coolant temperature. Other functions of the coolant temperature
signal are: Coolant Temperature Sensor
• Idle speed adjustment via the IAC
• Modify spark advance
• Electric cooling fan operation
1.12 Oxygen Sensor
The oxygen sensor (also known as a Lambda sensor) is located in the exhaust manifold and
its function is to measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. The sensor is an
electrochemical cell, which develops a voltage signal between its two electrodes that is
proportional to the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. The oxygen sensor adjusts and
maintains an optimum air fuel mixture to control the exhaust emission and the fuel
economy. When the oxygen content in the exhaust is high due to a lean mixture, the output
voltage of the sensor is close to zero. If the fuel air mixture is on the rich side, the oxygen
content in the exhaust is low and the output voltage of the sensor approaches 1.0 volts.
Holley uses a 3-wire (heated) O
2
sensor.
Three-Wire Heated Oxygen Sensor


















