ENGINE <6A1> -
On-vehicle Service
11B-9
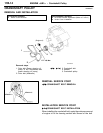
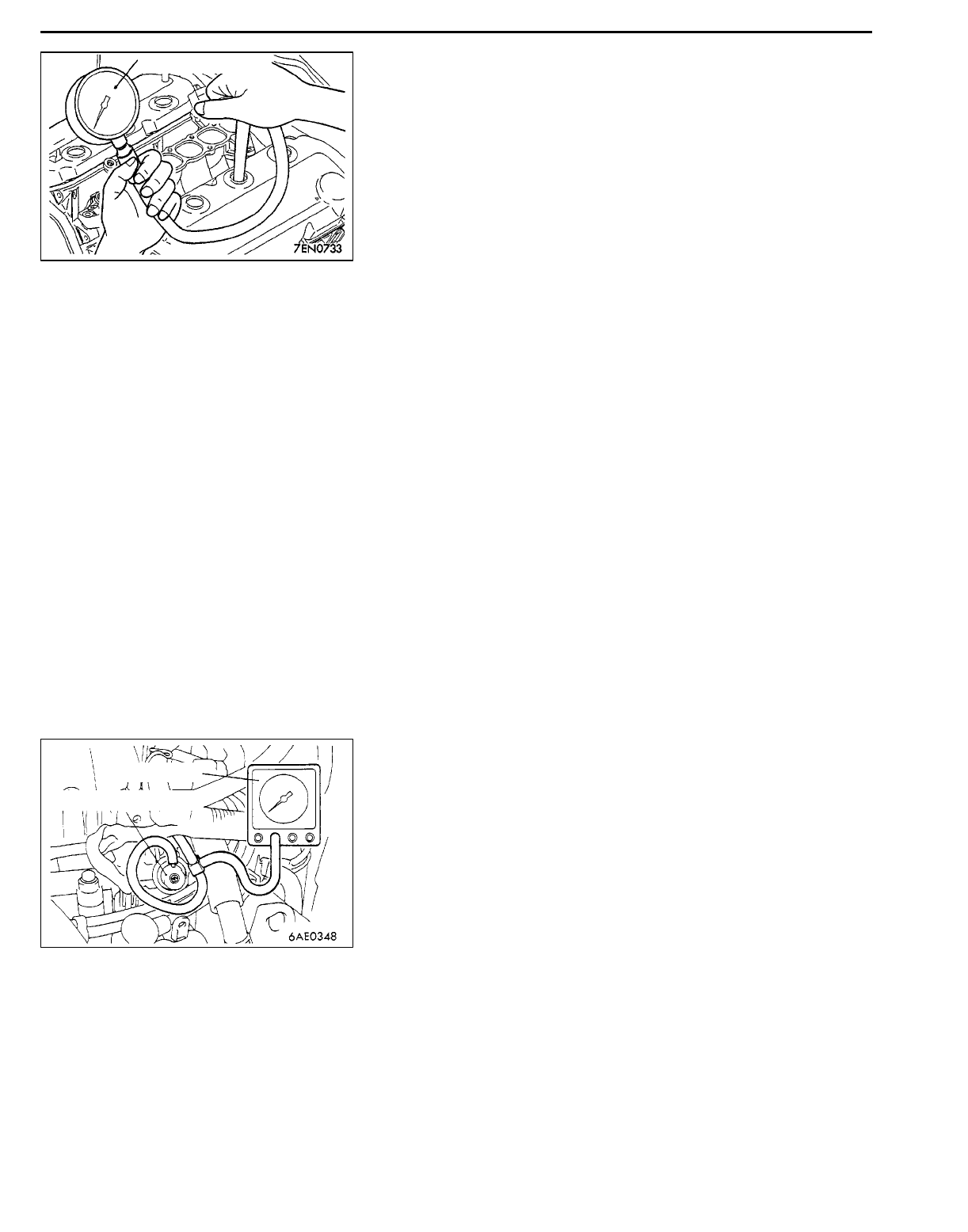
6. Set compression gauge to one of the spark plug holes.
7. Crank the engine with the throttle valve fully open and
measure the compression pressure.
Standard value (at engine speed of 250-400 r/min):
1,177 kPa
Limit (at engine speed of 250-400 r/min):
Min. 875 kPa
8. Measure the compression pressure for all the cylinders,
and check that the pressure differences of the cylinders
are below the limit.
Limit: Max. 98 kPa
9. If there is a cylinder with compression or a compression
difference that is outside the limit, pour a small amount
of engine oil through the spark plug hole, and repeat
the operations in steps 7 and 8.
(1) If the compression increases after oil is added, the
cause of the malfunction is a worn or damaged piston
ring and/or cylinder inner surface.
(2) If the compression does not rise after oil is added,
the cause is a burnt or defective valve seat, or pressure
is leaking from the gasket.
10. Connect the crank angle sensor connector.
11. Install the spark plugs and spark plug cables.
12. Use the MUT-II to erase the diagnosis codes.
NOTE
This will erase the diagnosis code resulting from the crank
angle sensor connector being disconnected.
MANIFOLD VACUUM CHECK
11100270393
1. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until the
temperature of the engine coolant reaches 80 to 95_C.
2. Connect a tachometer.
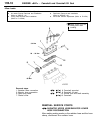
3. Attach a three-way union to the vacuum hose between
the fuel pressure regulator and the air intake plenum,
and connect a vacuum gauge.
4. Start the engine and check that idle speed is within the
standard value. Then read off the vacuum gauge.
Limit: Min. 60 kPa
Compression gauge
Vacuum gauge
Fuel pressure regulator