3-52 DISASSEMBLY, REASSEMBLY, INSPECTION, AND MAINTENANCE
Lubrication System
Breather
The function of the breather is to maintain a vacuum in the crankcase
to prevent the engine oil from being discharged outside the engine.
The breather valve regulates the flow of the air that is created by the
movement of the piston by allowing the air to flow from the inside of the
crankcase to the outside, while preventing the air from the outside of
the crankcase to enter inside.
In the rocker case, the maze and the volumetric expansion of the
rocker case causes the air containing oil to separate into oil and air.
The air from the crankcase ultimately flows to the air cleaner and mixes
with the intake air.
Inspection Method
•
With the rocker case installed in place, blow air or apply suction to
the breather pipe in order to activate the breather valve. Verify that
the breather valve closes when air is blown into the pipe.
•
Remove the retaining screws from the breather valve, and inspect the
valve and valve seat for the presence of damage, cracks, or wear.
•
Using a gap gauge, measure the clearance between the breather
valve and valve seat.
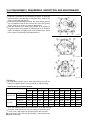
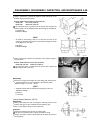
A: Rocker Case
B: Breather
C: Oil Level Sensor Terminal
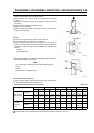
A: Breather Valve
B: Retaining Screw
Breather Valve Air Gap (maximum)
Service Limit: 0.2 mm (0.008 in)
If the air gap is greater than the service limit or if the breather valve
is defective, replace the breather valve with a new one.
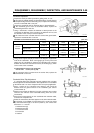
A: Retaining Screw
B: Backing Plate
C: Breather Valve
D: Air Gap
Air Filter (cartridge type)
With the cartridge type oil filter, the engine oil change interval can
be extended to 100 hours. (The engine oil must be changed every 50
hours in an engine without the cartridge type filter.)
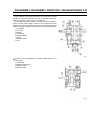
Ordinarily, the engine oil flows in the following order: entrance [A]
element [B] exit [C].
If the element becomes clogged, the oil flows through the bypass
[D], thus preventing the engine from operating without oil, although the
filtering function is bypassed.