Diatomic
Triatomic
Polyatomic
N
1.040
1 .ooo
0.941
=
A correction factor for the molecular structure of the gas
given by the following table:
Number of Atoms in the Gas Molecule
Monatomic
=
The temperature difference between the downstream and
upstream coils.
N
O’C).
AT
C,
is
given in the Tables (at
(Cal/gm);
=
The coefficient of specific heat of the gas
C,
(gm/min),
=
The mass flow rate of the gas
m
=
The constant amount of heat applied to the sensor tube,
(2)
H
P
N
mC
AT
H=
‘?eference ”
gas.
The K-factor is derived from the first law of thermodynamics
applied to the sensor tube.
where:
=
refers to the
)*
(
=
refers to the
“actual ” gas, and
),
(6),
(
“K”
factor defined in equation
=
The
0°C
and 760 mmHg(SCCM or SLM),
K
=
The volumetric flow rate of the gas referenced to standard
conditions of
Q
(1)
where:
Q,/Q,=K,/K,
the
tables, the following fundamental relationship is used:
so-
called “nasty” gas (i.e., toxic, flammable, corrosive, etc.).
Interpreting the reading of a flow controller which has been
calibrated with a gas other than the actual gas.
In applying
latly
useful if the actual gas is not a common gas or if it is a
patticu-
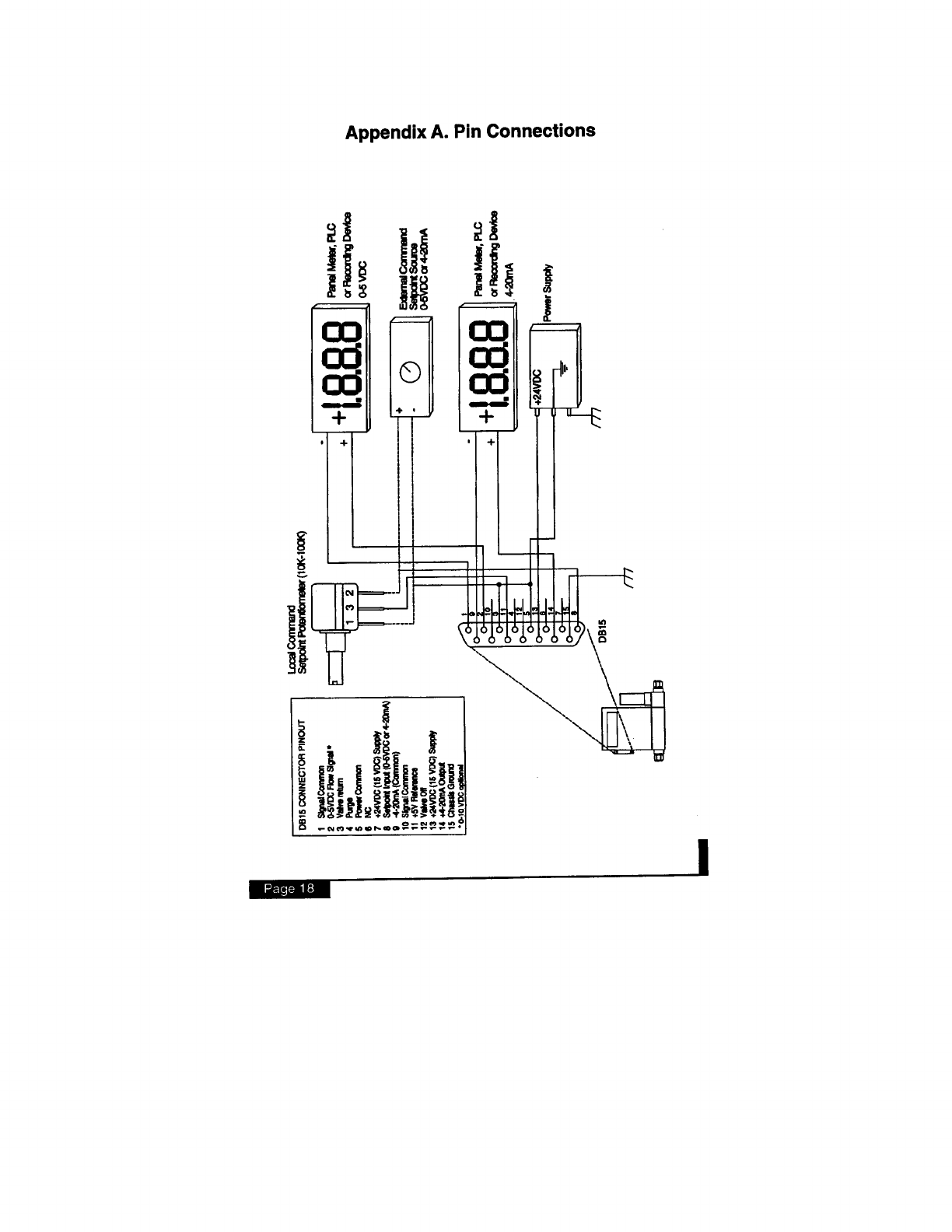
Appendix C. K-factors and Gas Tables
The following tables provide K-factors and thermodynamic
properties of gases commonly used with mass flow controllers
and meters. The purpose of these tables is two-fold:
1.
2.
Calibrating an “actual” gas with a reference gas. This is