78 Body
9-5
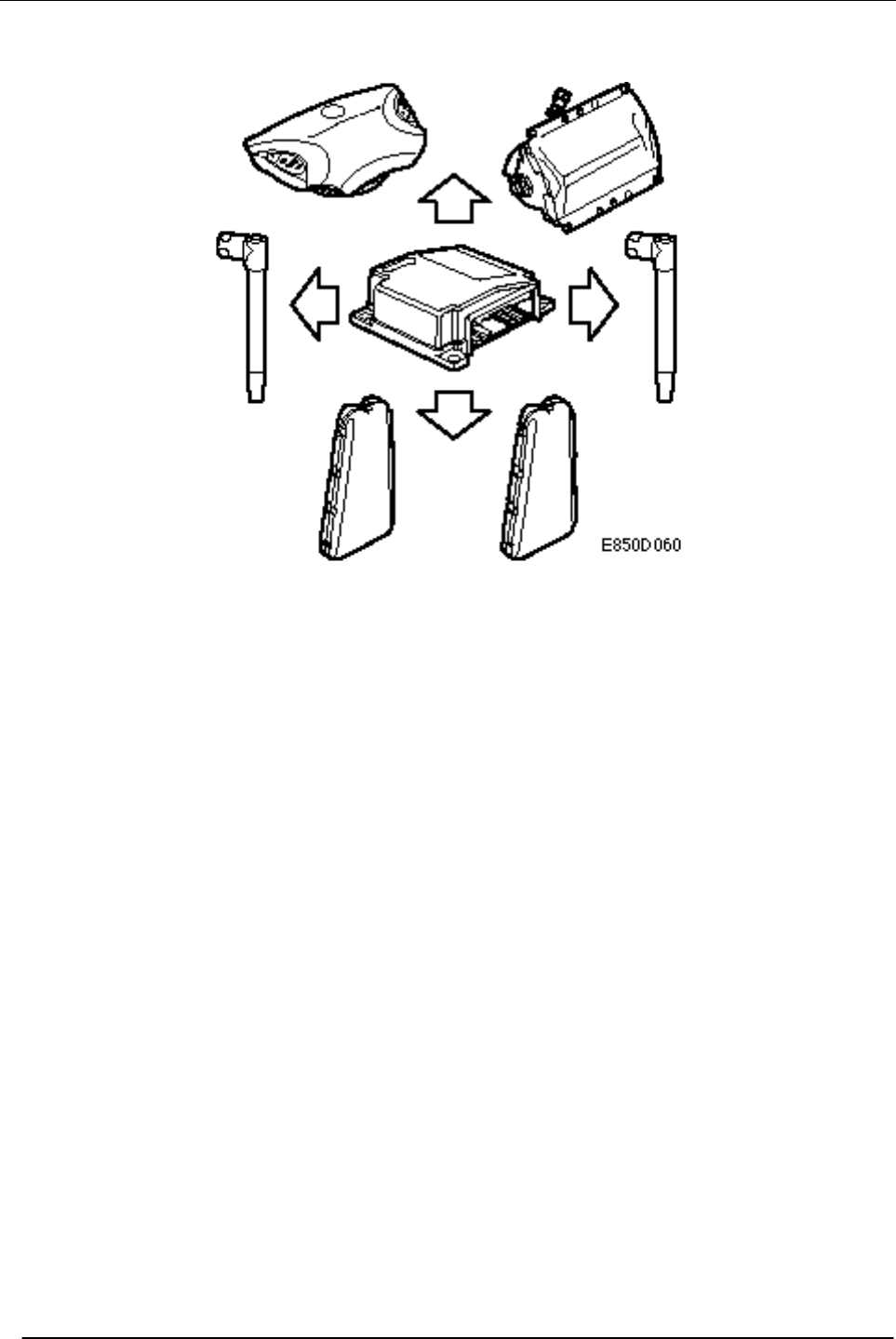
Control modules
The main task of the control module is to
recognize the situation arising from a collision
and inflate the airbag with the correct force
and/or ignite the correct seat-belt tensioner. The
control module contains two accelerometers, a
microprocessor, a reserve power source and a
voltage converter.
The control module has the capacity to activate
eight ignition circuits:
• Driver airbag, dual stage
• Passenger airbag, dual stage
• Side airbag, driver and passenger
• Seat-belt tensioner, driver and passenger
The activating time after a collision is different for
the various circuits.
The primary acceleration sensor measures the
acceleration and retardation forces in the
longitudinal and lateral directions of the car. The
secondary sensor measures the longitudinal
acceleration and retardation forces only.
The control module receives its information from
the two front impact sensors. The sensors are
located on the car's bumper member so that
collision forces can be detected as early as
possible.
A side impact sensor in each front door provides
information to the control module on collision
forces from the side. This information is provided
together with signals from the seat position
sensors and seat-belt buckle sensors for
calculating if, and how, the front airbags, side
airbags and belt tensioners should be activated.
If the seat-belt buckle is not locked or the seat is
far forward, the airbag will be inflated earlier than
normal. The seat-belt tensioner is activated only
if the seat-belt buckle is locked.
The front impact sensors contain an acceleration
sensor and a communication circuit for sending
information that is used by the control module. If
the values obtained from the impact sensors and
the control module accelerometers correspond
concerning collision force, the control module will
activate the seat-belt tensioners and airbags.