58 Brakes
9-5
Function, side acceleration sensor
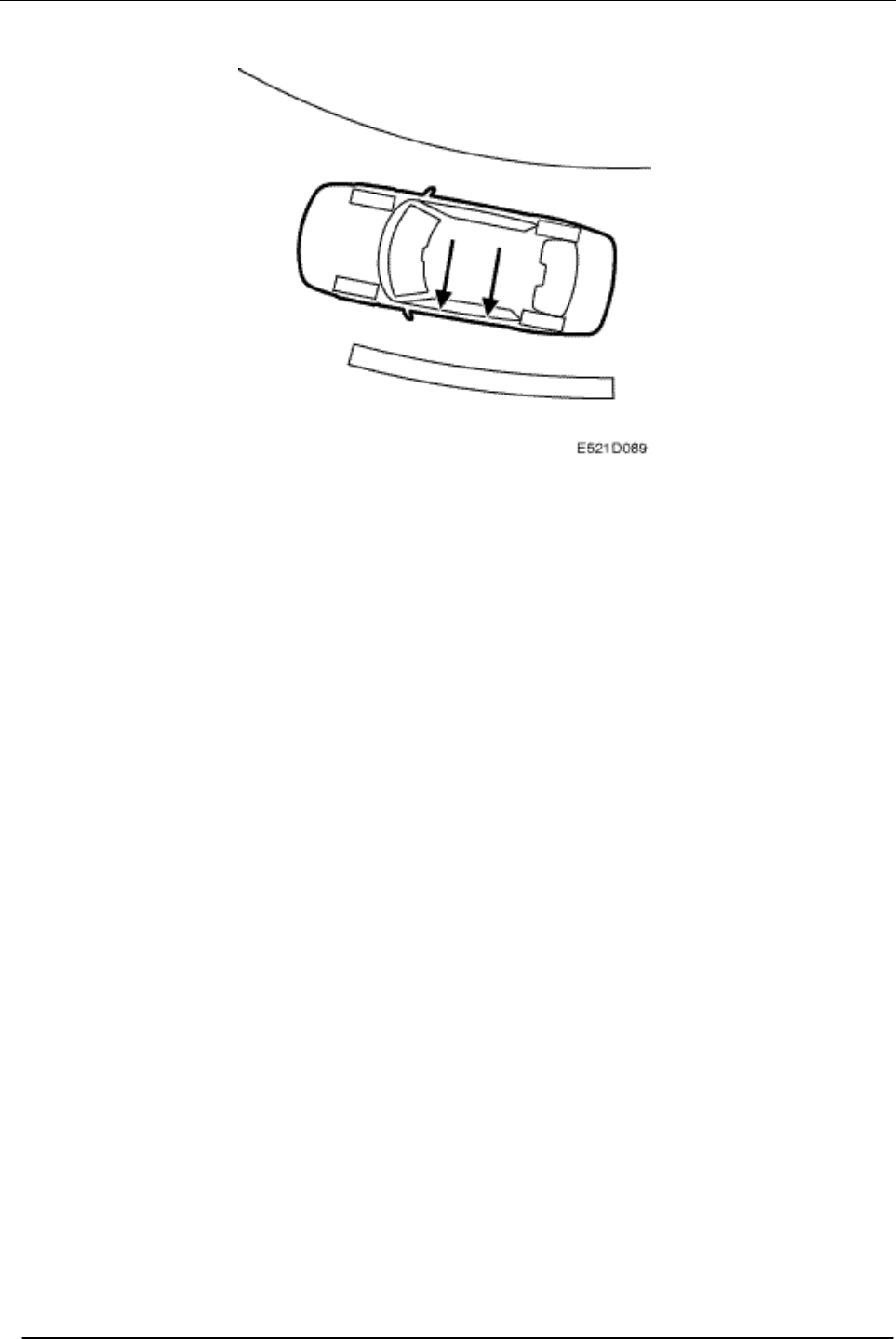
The side acceleration sensor registers the lateral
forces that arise during cornering. It provides the
ESP control module with information on the
magnitude of the lateral forces that are trying to
make the car change direction. It sends this
ACTUAL VALUE to the ESP control module,
which compares it with the DESIRED VALUE
given by the steering angle sensor.
A capacitive principle is used to measure the side
acceleration.
A capacitor plate with moveable mass is
suspended so that it can swing to and fro. On
either side of the moveable capacitor plates are
two more fixed capacitor plates. In this way, it is
constructed of two capacitors connected in
series. Electrodes are used to measure the
charge that the capacitors are able to store.
When the sensor is affected by side acceleration,
the capacitor with the moveable mass will move
towards the fixed capacitors and, thereby,
increase the charge in the capacitor towards
which the moveable mass is approaching
(measured in amperes).
Main components of side acceleration sensor
1. Fixed capacitors
2. Capacitor plate with moveable mass
3. Electrodes
Brake pressure sensor
The brake pressure sensor is located on the ESP
unit and is connected between the master
cylinder and the ESP unit. It measures the input
brake pressure from the master cylinder primary
circuit (FL & RR) up to 250 bar (3,626 psi).
The ESP control module uses the information on
the current brake pressure in order to calculate
the correct braking force on the wheels.