56 Brakes
9-5
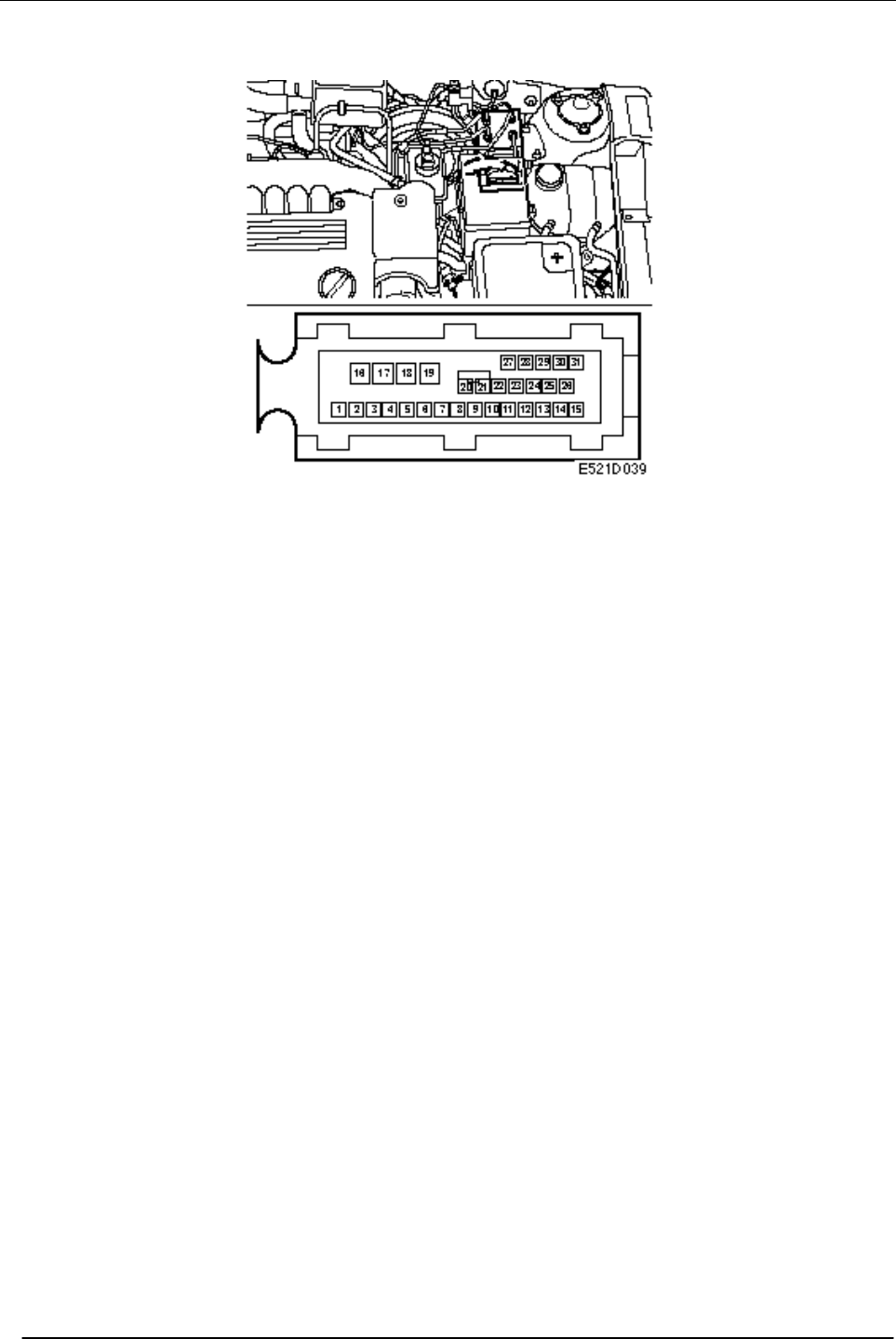
Control module
The control module is integrated in the ESP unit
and has a 31-pin connector. The control module
also governs the coordinated functions of ABS,
EBD and TCS.
The ESP function reduces engine torque and
handles the braking on all four wheels. Torque
reduction takes place after the ESP control
module sends a bus message requesting a
certain engine torque. The engine control module
uses this request to regulate the air
mass/combustion.
The stabilizing action of the ESP system is based
on calculations made in the control module
microprocessor. The control module evaluates
the information from the system sensors: wheel
speed sensors, steering angle sensor, yaw rate
sensor, side acceleration sensor and pressure
sensor. Data from these sensors informs the
control module of the driver's intentions, e.g. the
direction in which the driver wants to go, if the
driver is braking, etc.
These values are processed in the control
module, which continuously calculates the course
(ACTUAL VALUE) and compares it with the
course determined by the driver with the steering
wheel (DESIRED VALUE).
• If the car starts to understeer (when the front
tends to continue straight ahead in a bend),
the inside rear wheel will be braked.
• If the car starts to oversteer (the rear tends to
drift out), the system will engage and brake
the outside wheel until the measured and the
calculated yaw rate correspond.
Programming
The ESP control module automatically reads all
the information concerning the engine and
transmission from DICE. Tech 2 is used to
program the chassis variant, sport or standard.
Steering angle sensor
The steering angle sensor is located on the
steering column, between the steering wheel and
the intermediate steering shaft with universal
joint. The sensor has its own microprocessor with
self-diagnosis and is connected to the P-bus. It is
used to send information on the steering angle
(+530° is turns to the right, -530° is turns to the
left).
The control module receives information
concerning the intention of the driver, i.e. steering
wheel rotation, and the control module calculates
the speed at which the steering wheel was
rotated. This information is very important to the
ESP control module, which has to calculate a
possible regulation using this DESIRED VALUE.