61
MN002000A © 2004 Navman NZ Ltd. All rights reserved. Proprietary information and specifications subject to change without notice.
used to identify previously healthy satellites and
to generate “working” visible satellite lists, while
frequency standard data minimises satellite
acquisition uncertainties.
4.4.4 Frozen start
This state is entered if there are no valid data
sources available (SRAM, RTC, EEPROM). This
is considered to be a recovery mode because
EEPROM should always contain valid information.
An “out-of-the-box” board or a unit that has not
operated for a significant amount of time (months)
may approximate this state because the data in
EEPROM may be valid but expired or partially
complete.
4.5 Satellite management
This section describes the satellite management
functions of the Jupiter family of GPS receivers.
4.5.1 Visible list generation.
A list of satellites visible to the receiver antenna
is maintained whenever possible. A satellite is
considered visible if its elevation in the sky is
known to be above the horizon, if its almanac and
ephemeris data indicate it is healthy, and if it has
not been excluded by manual candidate satellite
specification. Note that although a satellite is
visible, its measurement is only available for use if
the satellite is above the elevation mask angle.
The receiver’s channel resources are directed
toward acquiring only those satellites which appear
in this list except when the receiver is in cold start
mode. Satellites within the list are ordered from
highest to lowest elevation which, for sequential
acquisition, also dictates the order in which
acquisition attempts are made.
Receiver position and current time are required
to compute satellite positions from orbital data.
If position and/ or time is not considered to be
well known (i.e. their expected errors are large),
then the list is extended below the horizon
and is filled to the maximum of 12 satellites. If
DGPS corrections are available, the satellites
represented in the corrections are used to set the
list membership instead, since they also represent
satellites visible to a nearby transmitting DGPS
base station.
New visible satellite lists are generated by
events that could cause a change in satellite list
membership or could indicate a significant change
in a satellite position relative to the antenna. These
events include receipt of an elevation mask angle
or candidate satellite specification command,
downloading of a new satellite almanac, and
changes in satellite health status reflected in new
almanac or ephemeris data.
In the case where DGPS corrections are used to
establish list membership, a change in the set of
satellites reflected in the corrections also causes a
new list to be generated. During initial acquisition,
a new list is generated when the receiver makes
step adjustments to position and time. In the
absence of these events, the visible satellite list is
updated every 30 seconds. The visible satellite list
is output in the Visible Satellites message (binary
Message 1003)
4.5.1.1 Dilution Of Precision (DOP)
Geometric Dilution of Precision (GDOP) is a
measure of the quality of a satellite constellation
geometry. GDOP reflects the influence of satellite
geometry on the accuracy of user position and
time estimates. The best geometry is that which
produces the lowest GDOP value. GDOP acts as a
multiplier of the error in position and time estimates
due to other sources.
GDOP is a composite measure. It can be
separated into:
• Position Dilution of Precision (PDOP)
PDOP reflects the effects of geometry on
three-dimensional position estimates
• Time Dilution of Precision (TDOP)
TDOP reflects geometric effects on time
estimates. The relationship can be expressed
as:
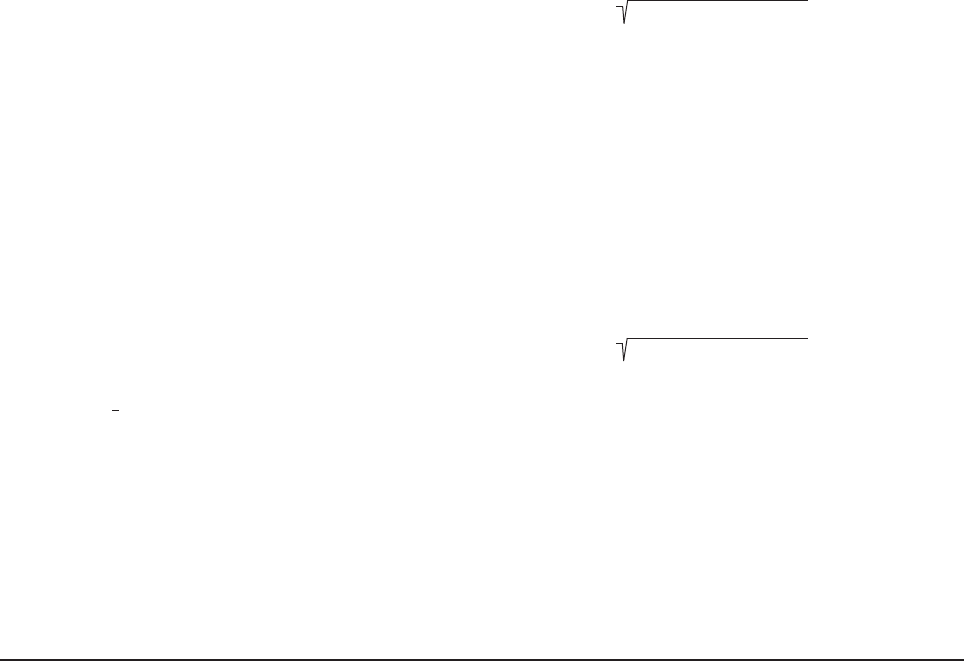
GDOP =
In turn, PDOP can be separated into horizontal
and vertical components:
• Horizontal Dilution of Precision (HDOP)
• Vertical Dilution of Precision (VDOP)
These components represent the effects of
satellite geometry on two-dimensional horizontal
position and on vertical position (altitude)
estimates, respectively.
This relationship can be expressed as:
PDOP =
The receiver computes the best available
GDOP and each of its components in the Visible
Satellites message (binary Message 1003). The
best available GDOP is that associated with
the satellite constellation consisting of all visible
satellites above the mask angle (satellites whose
measurements may be used).
At least four satellites are required to estimate
position and time, and therefore to compute a
(PDOP)
2
+ (TDOP)
2
(HDOP)
2
+ (VDOP)
2


















