4
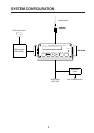
Figure 1 DGPS concept
HOW DGPS WORKS
Position accuracy for civil users of GPS is
limited to about 50 meters. This limitation
exists not only because of the US Depart-
ment of Defense's intentional downgrading
of the accuracy but also because of signal
attenuation and clock error inherent in both
GPS satellites and GPS receivers. With Dif-
ferential GPS (DGPS), however, differen-
tial corrections can improve position
accuracy to better than 10 meters.
Differential GPS is based upon accurate
knowledge of the accurate geographical lo-
cation of a reference station which is used
to compute corrections to GPS parameters,
error sources and resultant positions. These
differential corrections are transmitted to
GPS users, who apply the corrections to their
received GPS signals or computed position.
The DGPS reference stations are fixed at a
geodetically surveyed position. The refer-
ence station tracks all satellites in view,
downloads ephemeric data from them, and
computes corrections based on its measure-
ment and geodetic position. These correc-
tions are then broadcast to GPS users by
radio beacons (transmitters) to improve their
position solution.
The radio beacons broadcast in the fre-
quency range of 283.5–325 kHz and have a
transmitting range from 40 nm to 300 nm
depending on radio beacon.
Reference
station
Corrected data
DGPS Beacon receiver
(GR-80)
GPS
receiver
Radio beacon
(transmitter)
GPS satellite
GPS signal