- 9 -
5. THROTTLE BODY
5-1 SPECIFICATIONS
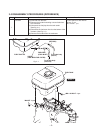
This engine is equipped with electronic fuel injection.
The fuel system consists of a throttle body assembly, power generation module, wire harness,
crankcase air pulse hose, fuel pressure return pipe and a fine mesh fuel filter.
The fuel system is calibrated after careful testing for optimum all-round performance (including
starting, acceleration, fuel consumption, output power characteristics).
The throttle body monitors air and engine temperature at start up and performs the choke
function automatically.
While the engine is in operation, the throttle body monitors engine speed, throttle position,
intake air temperature, and engine temperature to ensure proper engine performance.
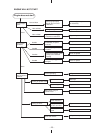
5-2 FUNCTIONS AND CONSTRUCTION
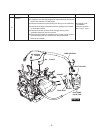
5-2-1 FUEL PUMP
The fuel pump chamber is located below the throttle body.
The fuel pump is actuated by crankcase vacuum from the cylinder head nipple through the
crankcase air pulse hose, to a nipple located on the fuel pump.
The fuel flows from the tank into the fuel pump. When the fuel pump is actuated by the
crankcase vacuum, the fuel is pressurized by the pump and pushed into the throttle body
pressure port.
5-2-2 FUEL PRESSURE REGULTOR
After the fuel pressure port is a diaphragm-type fuel pressure regulator.
The fuel pressure regulator relieves the throttle body of any excess fuel pressure and returns
excess fuel pressure back to the fuel tank through the fuel pressure return pipe.
5-2-3 FUEL INJECTOR
The throttle body pressure port feeds fuel at a regulated pressure to the fuel injector.
Fuel is metered by the fuel injector that is actuated electronicall
y by the Electronic Control Unit
(ECU).
The fuel is injected into the throttle bore and mixed with air from the air cleaner.
5-2-3 ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT (ECU)
The ECU (electronic control unit) on top of the throttle body is powered by the power generation
module when the engine is first rotated on start-up.
The ECU monitors engine conditions such as engine speed, throttle position, intake air
temperature, and engine temperature.
With these inputs, the ECU actuates the fuel injector to ensure the fuel/air mixture is of optimum
concentration and is fed into the combustion chamber of the engine at the correct timing.
The ECU also controls the low oil sensor system and monitors engine hours and other critical
engine data.