1-33
CAUTION:
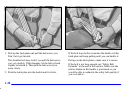
Smaller children and babies should always be
restrained in a child or infant restraint. The
instructions for the restraint will say whether
it is the right type and size for your child.
A very young child’s hip bones are so small that
a regular belt might not stay low on the hips,
as it should. Instead, the belt will likely be over
the child’s abdomen. In a crash, the belt would
apply force right on the child’s abdomen, which
could cause serious or fatal injuries. So, be sure
that any child small enough for one is always
properly restrained in a child or infant restraint.
Infants need complete support, including support for
the head and neck. This is necessary because an infant’s
neck is weak and its head weighs so much compared
with the rest of its body. In a frontal crash, an infant
in a rear
-facing restraint settles into the restraint, so the
crash forces can be distributed across the strongest part
of the infant’s body, the back and shoulders. A baby
should be secured in an appropriate infant restraint.
This is so important that many hospitals today won’t
release a newborn infant to its parents unless there is
an infant restraint available for the baby’s first trip in a
motor vehicle.