Trailering may be limited by the vehicle’s ability to carry
tongue weight. Tongue weight cannot cause the vehicle
to exceed the GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating) or
the RGAWR (Rear Gross Axle Weight Rating). The effect
of additional weight may reduce the trailering capacity
more than the total of the additional weight.
Consider the following example:
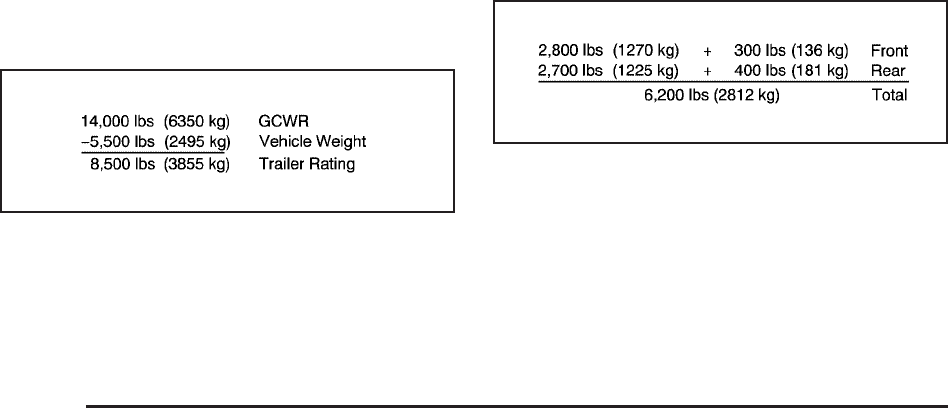
A vehicle model base weight is 5,500 lbs (2 495 kg);
2,800 lbs (1 270 kg) at the front axle and 2,700 lbs
(1 225 kg) at the rear axle. It has a GVWR of 7,200 lbs
(3 266 kg), a RGAWR of 4,000 lbs (1 814 kg) and a
GCWR (Gross Combination Weight Rating) of
14,000 lbs (6 350 kg). The trailer rating should be:
Expect tongue weight to be at least 10 percent of trailer
weight (850 lbs (386 kg)) and because the weight is
applied well behind the rear axle, the effect on the
rear axle is greater than just the weight itself, as much
as 1.5 times as much. The weight at the rear axle
could be 850 lbs (386 kg) X 1.5 = 1,275 lbs (578 kg).
Since the rear axle already weighs 2,700 lbs (1 225 kg),
adding 1,275 lbs (578 kg) brings the total to 3,975 lbs
(1 803 kg). This is very close to, but within the limit for
RGAWR as well. The vehicle is set to trailer up to
8,500 lbs (3 856 kg).
If the vehicle has many options and there is a front seat
passenger and two rear seat passengers with some
luggage and gear in the vehicle as well. 300 lbs (136 kg)
could be added to the front axle weight and 400 lbs
(181 kg) to the rear axle weight. The vehicle now weighs:
Weight is still below 7,200 lbs (3 266 kg) and you
might think 700 additional pounds (318 kg) should be
subtracted from the trailering capacity to stay within
GCWR limits. The maximum trailer would only be
7,800 lbs (3 538 kg). You may go further and think the
tongue weight should be limited to less than 1,000 lbs
(454 kg) to avoid exceeding GVWR. But the effect on
the rear axle must still be considered. Because the rear
axle now weighs 3,100 lbs (1 406 kg), 900 lbs (408 kg)
can be put on the rear axle without exceeding RGAWR.
5-48