- 40 -
6F8A0883
8. Principle of Operation
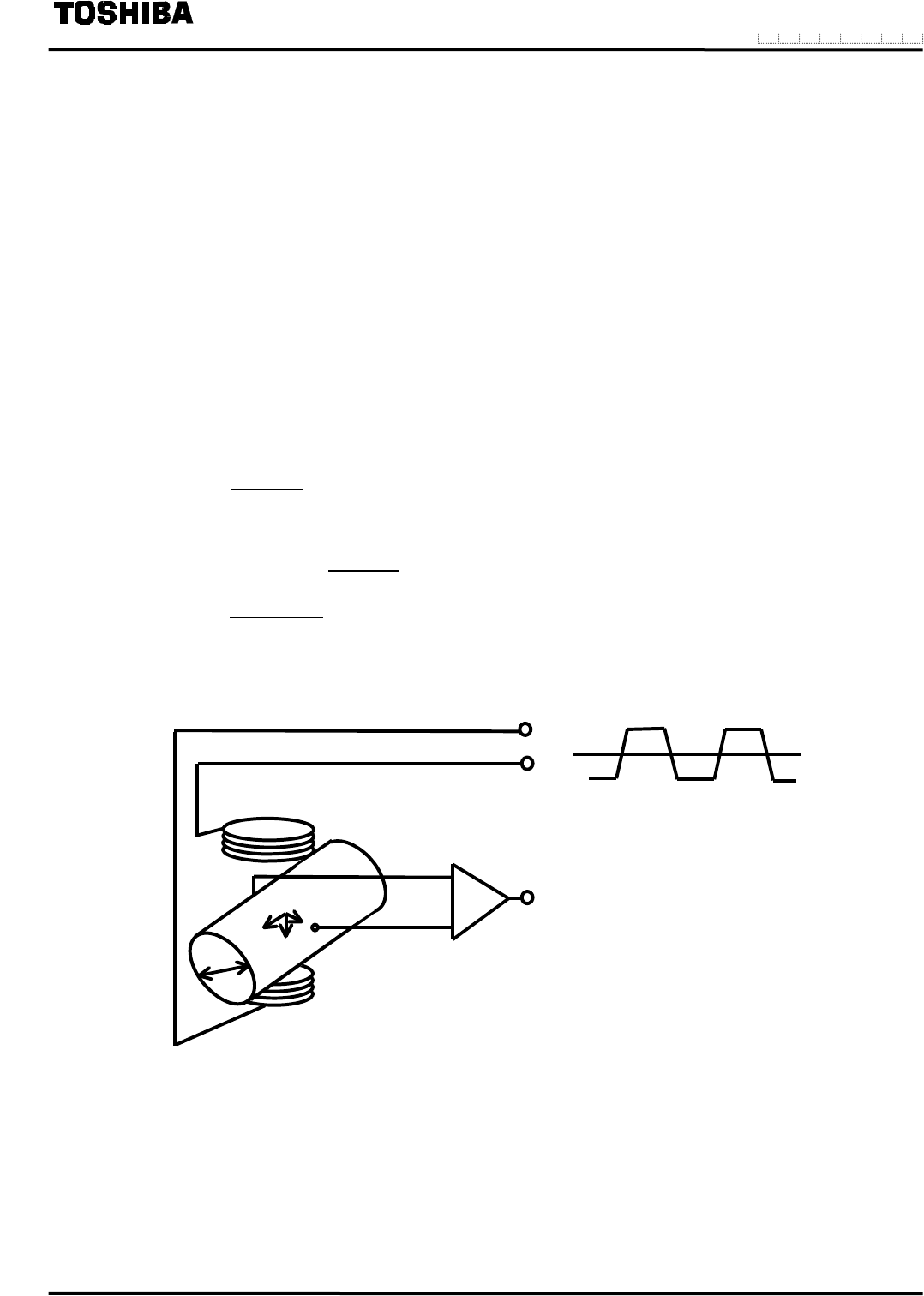
The operating principle of the electromagnetic flowmeter is based on Faraday's Law of electromagnetic
induction and it is designed to measure the volumetric flow rate of fluid. An insulated pipe of diameter D is
placed vertically to the direction of a magnetic field with flux density
B (see Figure 8.1). When an electrically
conductive fluid flows in the pipe, an electrode voltage E is induced between a pair of electrodes placed at right
angles to the direction of magnetic field. The electrode voltage E is directly proportional to the average fluid
velocity V.
The following expression is applicable to the voltage.
E = K × B × D × V [V] ........ (Eq. 8.1)
Volumetric flow rate Q [m
3
/s] is:
Q = × V ................(Eq. 8.2)
Using the Equation 8.1 and 8.2
E = K × B × D × × Q
E = × Q ............(Eq. 8.3)
Therefore, volumetric flow rate is directly proportional to the induced voltage.
Figure 8.1 Principle of Operation
The GF630/LF600F, GF630/LF610F and GF632 use the square-wave excitation method, which
provides long-term
stable operation. With square-wave excitation, the GF630/LF600F, GF630/LF610F and GF632 offers reliable
measurement without being affected by electrostatic or electromagnetic interference, or electrochemical
polarization between the electrodes and the fluid to be measured.
E = induced electrode voltage [V]
K = constant
B = magnetic flux density [T]
D = meter pipe diameter [m]
V = fluid velocity [m/s]
π × D²
4
4
π × D²
4 × K × B
π × D
Square-Wave Excitation
B
V
E
D