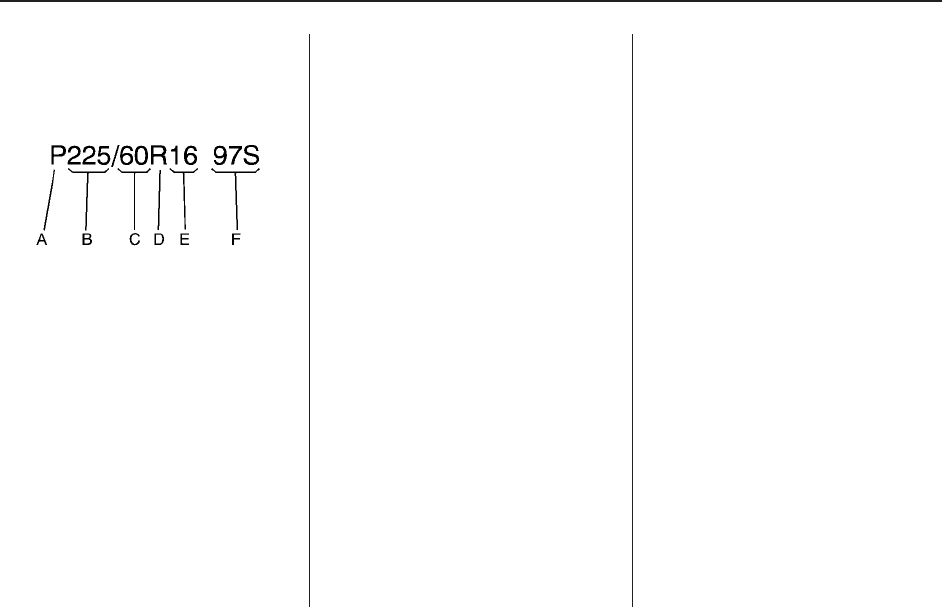
Tire Size
The following illustration shows
an example of a typical
passenger vehicle tire size.
(A) Passenger (P-Metric) Tire
:
The United States version of a
metric tire sizing system. The
letter P as the first character in
the tire size means a passenger
vehicle tire engineered to
standards set by the U.S. Tire
and Rim Association.
(B) Tire Width
: The three-digit
number indicates the tire section
width in millimeters from sidewall
to sidewall.
(C) Aspect Ratio
: A two-digit
number that indicates the tire
height-to-width measurements.
For example, if the tire size
aspect ratio is 60, as shown in
item C of the illustration, it would
mean that the tire’s sidewall is
60 percent as high as it is wide.
(D) Construction Code
: A letter
code is used to indicate the type
of ply construction in the tire.
The letter R means radial ply
construction; the letter D means
diagonal or bias ply construction;
and the letter B means
belted-bias ply construction.
(E) Rim Diameter
: Diameter of
the wheel in inches.
(F) Service Description
: These
characters represent the load
index and speed rating of the tire.
The load index represents the
load carry capacity a tire is
certified to carry. The speed
rating is the maximum speed a
tire is certified to carry a load.
Tire Terminology and
Definitions
Air Pressure: The amount of air
inside the tire pressing outward
on each square inch of the tire.
Air pressure is expressed in
pounds per square inch (psi)
or kilopascal (kPa).
Accessory Weight
: This means
the combined weight of optional
accessories. Some examples
of optional accessories are,
automatic transmission, power
steering, power brakes, power
windows, power seats, and air
conditioning.
Aspect Ratio
: The relationship
of a tire’s height to its width.
Belt
: A rubber coated layer of
cords that is located between the
plies and the tread. Cords may
be made from steel or other
reinforcing materials.
5-46 Service and Appearance Care