13
automatically default to the last beacon
transmitter used each time the GPS unit is turned
on.)
9. Select the Satellite Bar Graph Page. A “D” will
appear at the bottom of the signal strength bar
for each satellite with a corresponding differen-
tial correction or “3D Differential” will be
displayed at the top of the satellite page. This
page is useful for determining the quality of
differential coverage available. (Remember, the
more satellites with corresponding differential
corrections, the more accurate your position will
be.)
Reference
After entering the beacon’s
operating frequency, set the
bit rate as indicated on the
Beacon Reference Card.
Beacon information is also
available from the other
sources listed on the card.
DGPS:
How It Works
DGPS: How It Works
Differential GPS (DGPS) is a technique used to
improve the accuracy of the Global Positioning System.
DGPS reduces the effects of Selective Availability(SA),
ionospheric variations and can improve position accuracy
to better than 10 meters.
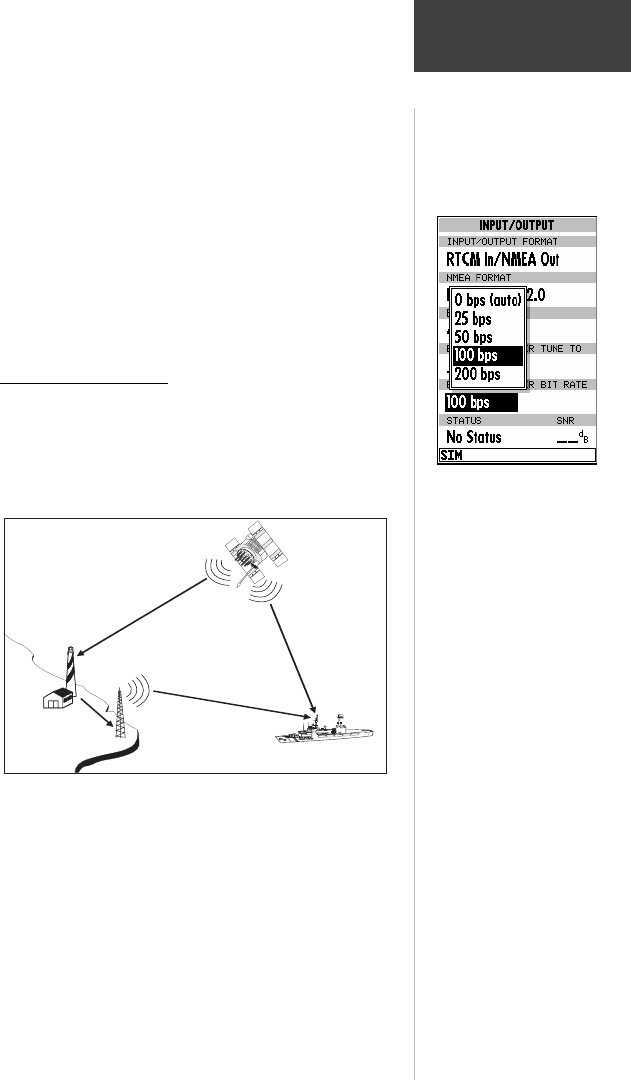
Figure 4: The DGPS System
A DGPS system consists of the following:
• DGPS Beacon Transmitter and GPS Receiver at
a known location
• Shipboard DGPS Beacon Receiver
• Shipboard GPS Receiver (DGPS capable)
• GPS Satellites
GPS SIGNAL
GPS SIGNAL
DGPS (CORRECTION) SIGNAL
SHIPBOARD GPS AND
DGPS RECEIVERS
CORRECTION
DATA
GPS RECEIVER
STATION AND
DGPS TRANSMITTER


















