ENGLISH
18
A
B
C
D
1
Basic suspension setup for the weight of the driver
To achieve maximum handling performance and to prevent the telescopic
fork and shock absorber from being damaged, the basic setup of the
suspension components must be suitable for your child's weight. At delivery,
KTM's mini motorcycles are set to accommodate a driver weighing 25 - 30
kg (wearing full protective clothing). If your child's weight exceeds or falls
short of this range, you will need to adjust the spring preload for the
telescopic fork and shock absorber accordingly.
To adjust, check the sag of the shock absorber and telescopic fork. The
motorcycle should be filled up and your child should be wearing full
protective clothing.
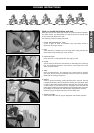
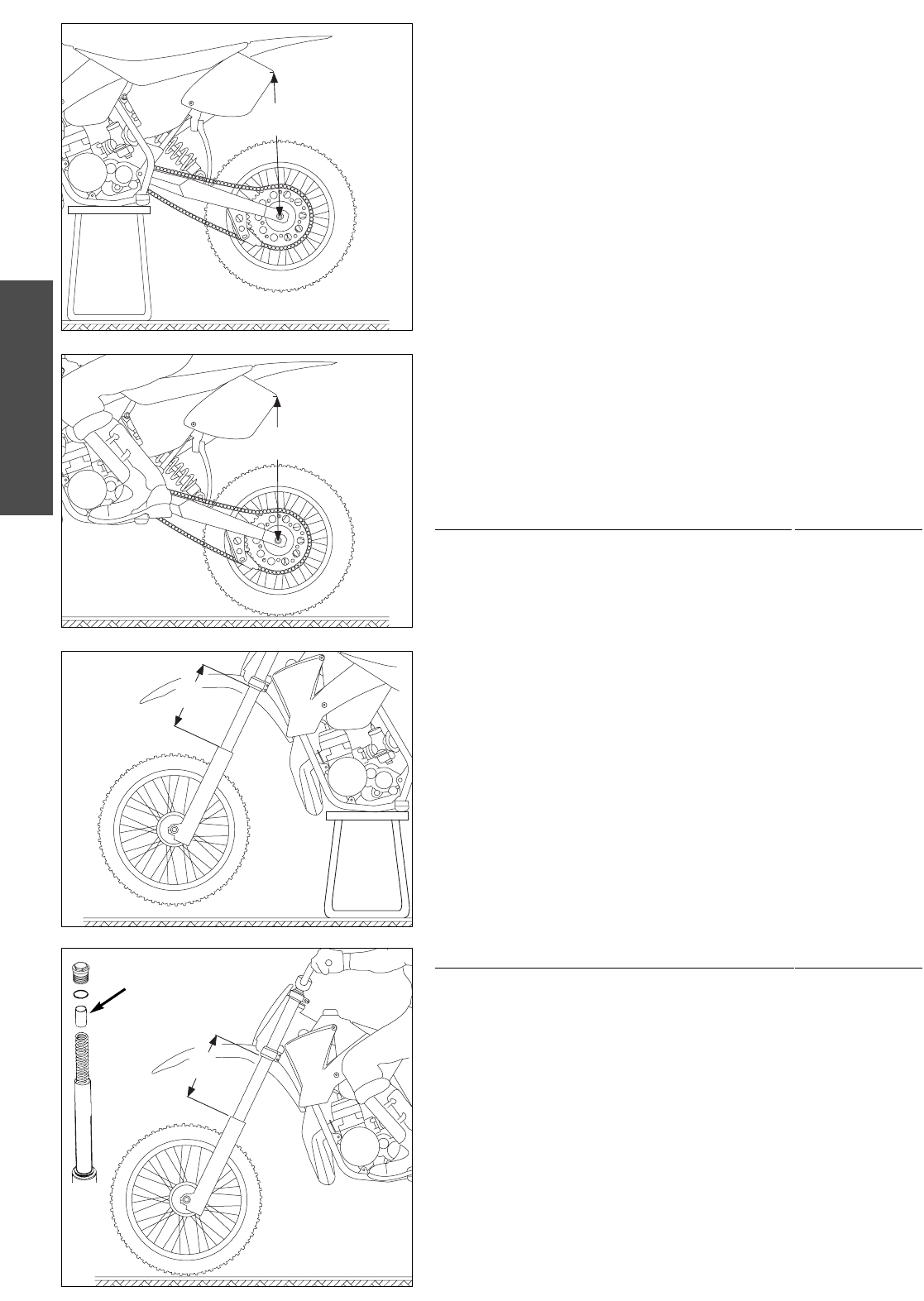
To determine the sag of the shock absorber
– Jack up the motorcycle until the rear wheel no longer touches the ground.
– Measure the vertical distance between the rear wheel axle and a fixed
point (e.g. a mark on the side cover) and write it down as dimension A.
– Place the motorcycle on the ground again.
– Have your child sit on the motorcycle in a normal seating position (feet on
the footrests) wearing full protective clothing and bounce up and down a
few times to allow the rear wheel suspension to become level.
– Holding your child and the bike, have another person measure the
distance between the same two points with the load on the motorcycle to
establish dimension B.
– The sag is the difference between dimensions A and B.
EXAMPLE:
Motorcycle jacked up (dimension A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .400 mm
Motorcycle on ground with driver seated (dimension B)
. . . . . . .– 355 mm
Sag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45 mm
50 SX Pro Junior LC shock absorber sag. . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 mm (± 5 mm)
50 SX Pro Senior LC shock absorber sag . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 mm (± 5 mm)
If the sag is lower, the spring preload of the shock absorber must be reduced,
if the sag is higher, the spring preload must be increased. A harder spring is
also available for the 50 SX Pro Senior LC (see spare parts catalog).
To determine the sag of the telescopic fork
– Jack up the motorcycle until the rear wheel no longer touches the ground.
– Measure the distance between the upper edge of the slider tube and the
triple clamp and write it down as dimension C.
– Have your child sit on the motorcycle in a normal seating position (feet on
the footrests) wearing full protective clothing, and bounce up and down
a few times to allow the telescopic fork to become level.
– Holding your child and the bike, have another person measure the
distance between the same two points with the load on the motorcycle to
establish dimension D.
– The sag is the difference between dimensions C and D.
EXAMPLE:
Motorcycle jacked up (dimension C) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .200 mm
Motorcycle on ground with driver seated (dimension D)
. . . . . . .– 160 mm
Sag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40 mm
50 SX Pro Junior LC telescopic fork sag . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 mm (± 5 mm)
50 SX Pro Senior LC telescopic fork sag . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 mm (± 5 mm)
If the sag is lower, the spring preload of the telescopic fork must be reduced,
if the sag is higher, the spring preload must be increased.
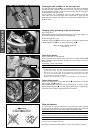
The preload on the fork spring is determined by the length of preload spacer
1. If an adjustment is necessary, demount the fork legs, remove the plugs
and shorten the pretensioning sleeves or replace with longer ones (see
maintenance of telescopic fork). Harder fork springs are also available for
both models (see spare parts catalog).