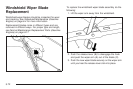
Inflation - Tire Pressure
Tires need the correct amount of air pressure to operate
effectively.
Notice: Do not let anyone tell you that
under-inflation or over-inflation is all right. It is not.
If your tires do not have enough air (under-inflation),
you can get the following:
• Too much flexing
• Too much heat
• Tire overloading
• Premature or irregular wear
• Poor handling
• Reduced fuel economy
If your tires have too much air (over-inflation), you
can get the following:
• Unusual wear
• Poor handling
• Rough ride
• Needless damage from road hazards
A Tire and Loading Information label is attached to the
vehicle’s center pillar (B-pillar), below the driver’s
door lock post (striker). This label lists your vehicle’s
original equipment tires and their recommended cold tire
inflation pressures. The recommended cold tire
inflation pressure, shown on the label, is the minimum
amount of air pressure needed to support your vehicle’s
maximum load carrying capacity.
For additional information regarding how much weight
your vehicle can carry, and an example of the tire
and loading information label, see Loading Your Vehicle
on page 4-48.
When to Check
Check your tires once a month or more. Do not forget to
check the spare tire. For additional information
regarding the spare tire, see Spare Tire on page 5-114.
How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type gage to check tire
pressure. You cannot tell if your tires are properly inflated
simply by looking at them. Radial tires may look properly
inflated even when they’re underinflated. Check the tire’s
inflation pressure when the tires are cold. Cold means
your vehicle has been sitting for at least three hours or
driven no more than 1 mile (1.6 km).
5-80