Chapter 3 Advanced Programming with NI-IMAQdx
NI-IMAQdx User Manual 3-6 ni.com
For GigE Vision cameras, you can configure the camera to broadcast or
multicast image data to all nodes on the network. Broadcast is not routable,
and everyone on the same network sees the data, even if they are not
listening. Multicast is routable if the network is configured properly. A
multicast configuration is preferred if supported by the camera because
only interested parties can see the data traffic.
Next, start the listener(s). On the listening computer, open your camera
interface with the 64-bit unique identifier of the target camera, which you
can find in the General tab in MAX. The controller can get a unique ID and
send it to the listener sessions. Additionally, you must set the listener
camera control mode parameter.
At this point, both the controller and listener systems are acquiring the
same live data from the same camera. When running as a listener, most
acquisition attributes are read-only. No camera feature or control is
accessible when running as a listener system. Attempts to set these
attributes result in the following error:
Attribute not writable.
There is no synchronization between the controller and the listener host
computers provided by the low-level driver. The user must start the
controller before starting the listener. If the camera is not transmitting
data when the listener initializes, the session returns the following error:
No acquisition in progress. If the controller stops the video feed of
the camera, the listener times out.
Scalable Image Size
Digital cameras support a predefined set of image sizes, which you can
select through the Acquisition attributes in MAX. Refer to your camera
documentation for a list of supported formats.
If you are using LabVIEW, the NI-IMAQdx software recognizes the
predefined formats and automatically allocates enough memory to
accommodate the image. The image is resized as necessary.
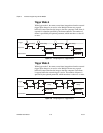
Some cameras support user-configurable ROI, which allows you to define
the size of the acquired image. If you use this format, you must input the
image size using the Region of Interest attributes—offset x, offset y,
width, and height. The size and position of the sub-image you are acquiring
must be a multiple of the Increment attribute, as shown in Figure 3-2,
or the driver acquires the smallest sub-image that contains the ROI you
defined.