TAIP
TAIP is an easy-to-use ASCII protocol developed by Trimble for vehicle tracking. The
user can set up polling schemes and mark GPS messages with unique identifiers. The
TAIP messages and output rates are user selectable and can be configured to operate on
either Port 1 or Port 2.
NMEA 0183
NMEA 0183 is an industry standard protocol common to marine applications. NMEA
provides direct compatibility with other NMEA-capable devices such as chart plotters,
radars, etc. The SV12 GPS Receiver supports most NMEA messages for GPS
navigation. NMEA messages and output rates can be user selected as required.
2.1.1 SV12 GPS Serial Port Interface
The GPS Receiver is a DCE (Data Communication Equipment) device. To connect to a
host computer, or DTE (Date Terminal Equipment) device, use a straight through cable.
To connect a Differential Radio (DCE device) to the receiver (DCE device) use a cross-
over cable or null modem cable. See Table 2.1.1-1
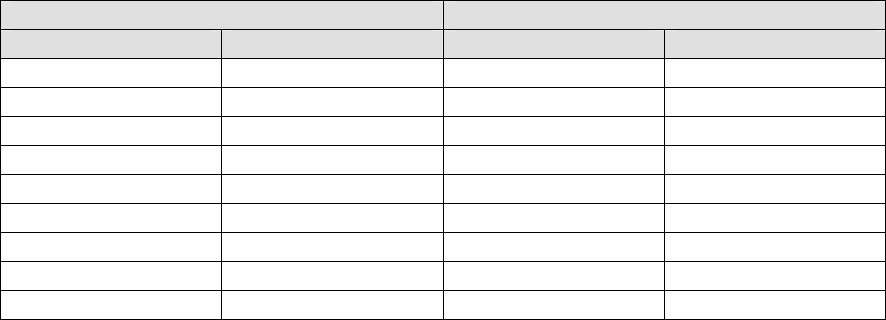
Table 2.1.1-1 Serial Port Pin-outs
Port 1 Port 2
Pin Description Pin Description
1 NC 1 NC
2 TX 2 TX
3 RX 3 RX
4 NC 4 NC
5 GND 5 GND
6 NC 6 NC
7 NC 7 NC
8 NC 8 NC
9 PPS Out 9 PPS Out
The PPS signal is an open collector interface on pin 9 of Ports 1 and 2. The polarity of
the PPS signal is an inverted, 10 µs negative going pulse with the falling edge
synchronized to UTC. One can use a 10 K pull-up resistor to pull-up the PPS.
2.2 Antenna
The GPS antenna receives the GPS satellite signal and passes them to the receiver.
Because the GPS signals are spread spectrum signals in the 1575 MHz range and do not
penetrate conductive or opaque surfaces, the GPS antenna must be located outdoors with
a clear view of the sky. The SV12 GPS Receiver requires an active antenna. The
received GPS signals are very low power, approximately 140 dB, at the surface of the
3















