Ground
6V
220AH
6V
220AH
6V
220AH
6V
220AH
6V
220AH
6V
220AH
Fuse(s)
Elite 5000W
Elite
™
5000W—Pure Sine Inverter by Wagan Tech
9
www.wagan.com
User’s Manual—Read before using this equipment
©2012 Wagan Corporation
All Rights Reserved.
Wagan Tech and wagan.com are trademarks used by Wagan Corporation.
10
hours example as above, then 50 amps is needed for 10 hours. This provides
us with the basic amp-hours (AH) of battery that is required. Ten hours at 50
amps equals 500 amp-hours (AH). There are additional factors that determine
actual run time. These include:
• AC appliance load and time in use (basic AH).
• Cable gauge and length (cable losses).
• Charge level of the batteries (between use, chargers have to be able to
fully charge the batteries).
• Temperature of the batteries (colder batteries provide fewer amps).
• Age and condition of the batteries (older batteries lose AH capacity).
• Compliance with turning off unnecessary AC loads.
• Use of DC appliances and compliance with turning off unnecessary DC
loads.
Derating the Battery Bank
Most lead-acid batteries have a rating expressed in amp-hours (AH). The most
common rating of AH is “at the 20 hour rate”.
NOTE: Despite several internet explanations, there is no relationship between
cold cranking amps (CCA) and ampere-hours (AH).
For example, if a 20 AH battery is discharged at a 1 amp rate, is will take 20
hours to discharge that battery. The terms “charged” and “discharged” relate
to actual battery voltage. This means that the output voltage of a nominal
12 volt battery starts at 13.4 volts (fully charged) then drops to 10.5 volts
(discharged). If the load on the battery causes the battery to discharge faster
than the 20 hour rate, the capacity (AH) of the battery is measurably reduced
(derated). In heavy battery discharge applications, double the estimated Amp
Hour rating and configure batteries to support this capacity. If the batteries
are frequently charged by an alternator, the Amp Hour rating of the batteries
required may be reduced.
Configuring the battery bank
Batteries that are used indoors or inside a vehicle or vessel, should be deep-
cycle, sealed lead acid batteries.
NOTE: It is important that for any inverter installation to battery protection
fuses. Battery fuses are added to the positive (+) battery cable as close as
possible to the battery bank’s positive terminal. The fuse amperage rating
must be sized to allow simultaneous operation of all the AC appliances
to be powered, plus 20 percent safety factor. Fuses are very important to
protect equipment, batteries and personnel. The fuses protect against battery
explosion if the cables that connect to the inverter accidentally short.
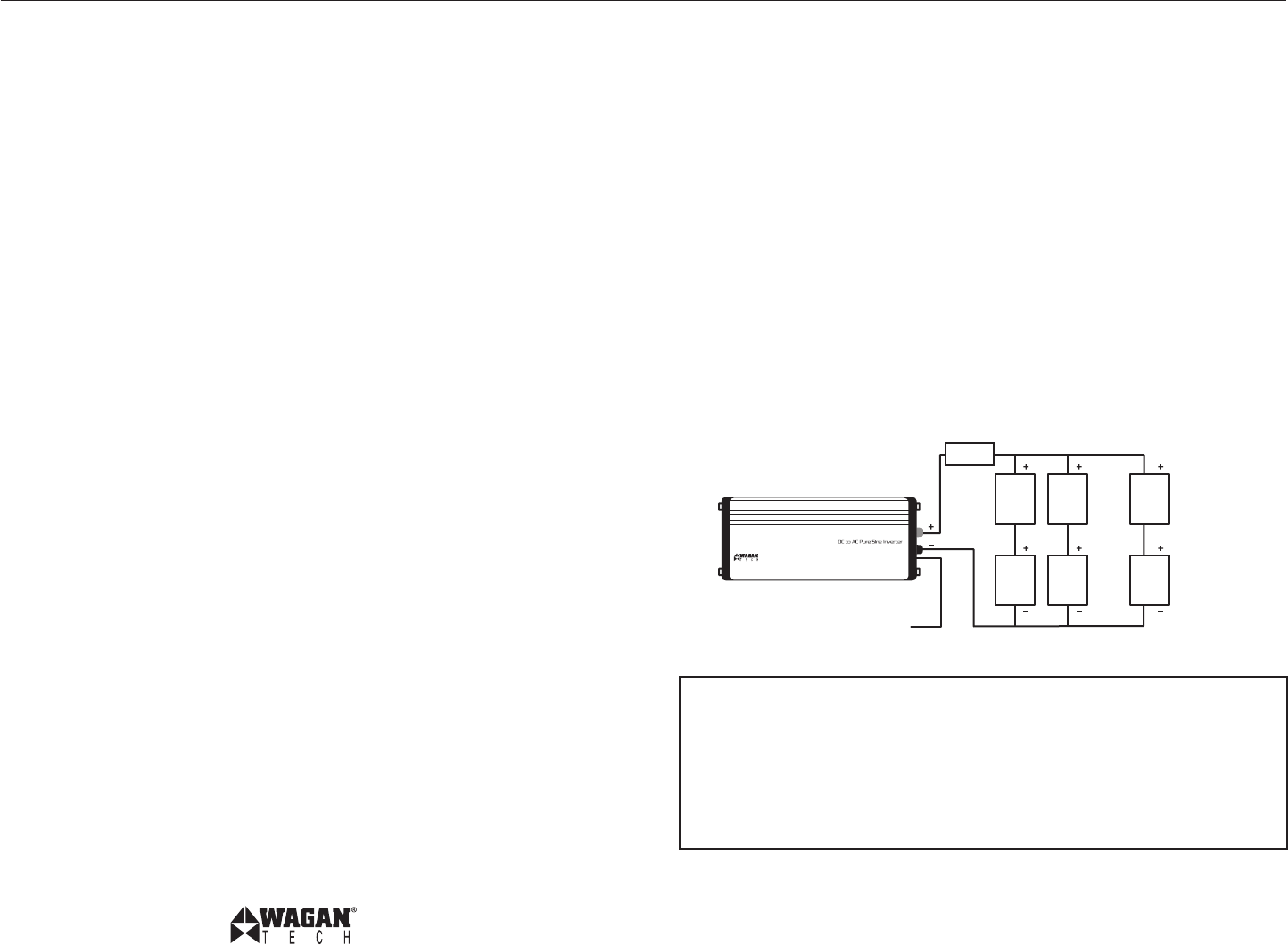
Battery Bank Diagram
This Battery Bank diagram shows the use of 6 Volt Golf Cart batteries wired to
deliver 12 Volts to the inverter. These batteries are flooded (venting) and vent
to outside air.
WARNING—Exploding Batteries!!
exploding baTTeries can spray molTen lead, hoT sulfuric acid, and
oTher meTal and plasTic fragmenTs. baTTeries ThaT are charging or
under high discharge raTes produce explosive hydrogen gas inTo The
surrounding area. be safe–fuse The baTTery bank and make sure The
baTTeries are properly venTilaTed.