GM-83 User’s manual
11
4.1.6 Course Over Ground and Ground Speed (VTG)
Table 4-10 contains the values for the following example:
$GPVTG,309.62,T, ,M,0.13,N,0.2,K*6E
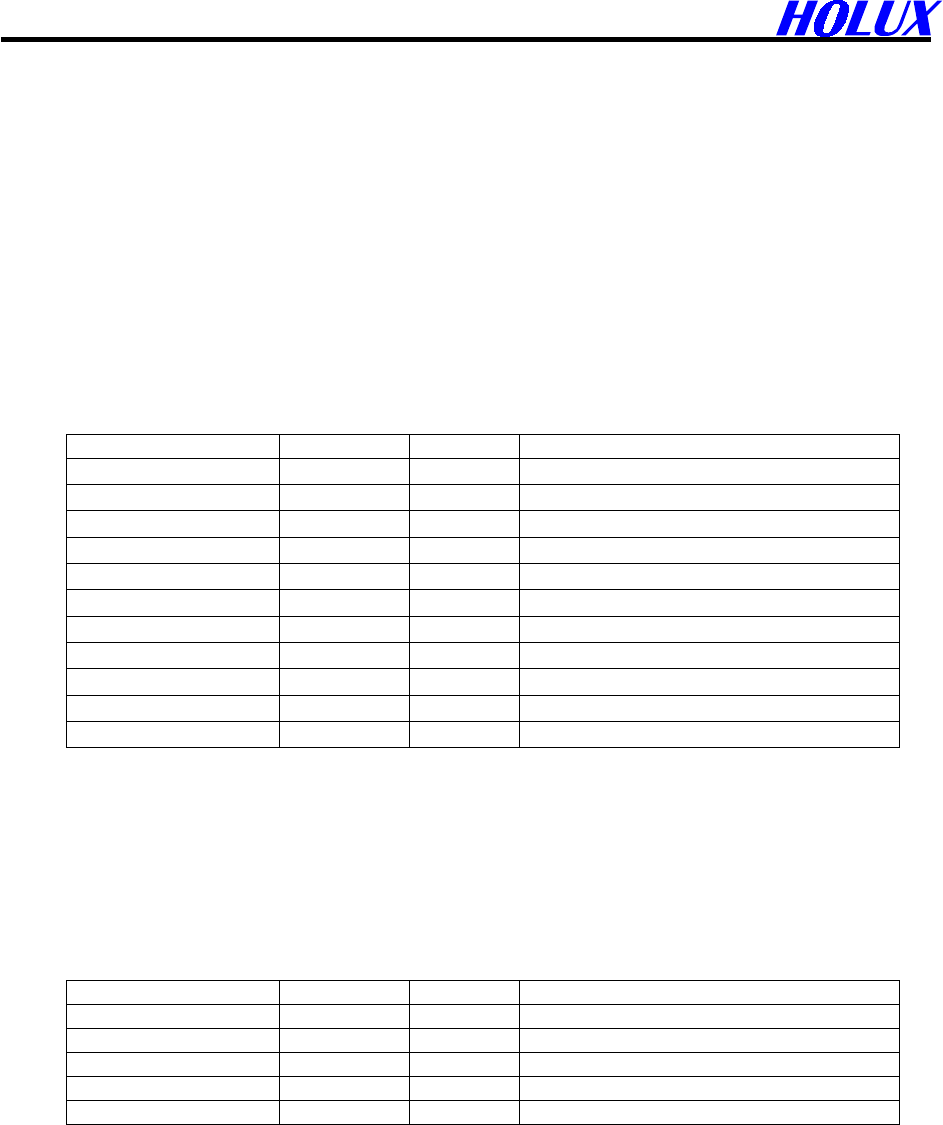
Table 4-10 VTG Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $GPVTG VTG protocol header
Course 309.62 degrees Measured heading
Reference T True
Course degrees Measured heading
Reference M Magnetic
(1)
Speed 0.13 knots Measured horizontal speed
Units N Knots
Speed 0.2 km/hr Measured horizontal speed
Units K Kilometers per hour
Checksum *6E
<CR> <LF> End of message termination
(1). SiRF Technology Inc. does not support magnetic declination. All “course over ground” data are geodetic WGS84
directions.
4.1.6 MSK Receiver Signal (MSS)
Table C-9 contains the values for the following example:
$GPMSS,55,27,318.0,100,*66
Table C-9 MSS Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $GPMSS MSS protocol header
Signal Strength 55 dB dB SS of tracked frequency
Signal-to-Noise Ratio 27 dB SNR of tracked frequency
Beacon Frequency 318.0 kHz Currently tracked frequency
Beacon Bit Rate 100 100 bits per second
Note – The MSS NMEA message can only be polled or scheduled using the MSK NMEA input message.
4.2 RTCM Received Data
The default communication parameters for DGPS Input are 9600 baud, 8 data bits, stop bit, and no
parity. Position accuracy of less than 5 meters can be achieved with the GM-83 by using Differential GPS
(DGPS) real-time pseudo-range correction data in RTCM SC-104 format, with message types 1,2, or 9. As
using DGPS receiver with different communication parameters, GM-83 may decode the data correctly to
generate accurate messages and save them in battery-back SRAM for later computing.
















