9
Table 2 — Electrical Data
LEGEND
*Fuse or HACR circuit breaker.
NOTES:
1. In compliance with NEC requirements (U.S.A. Standard) for
multimotor and combination load equipment (refer to NEC Arti-
cles 430 and 440), the overcurrent protective device for the unit
shall be fuse or HACR breaker.
2.
Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply volt-
age is greater than 2%.
Use the following formula to determine
the percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance
Example: Supply voltage is 400-3-50.
AB = 393 v
BC = 403 v
AC = 396 v
= 397
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 397 – 393 = 4 v
(BC) 403 – 397 = 6 v
(AC) 397 – 396 = 1 v
Maximum deviation is 6 v.
Determine percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
= 1.5%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the
maximum allowable 2%.
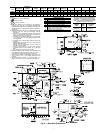
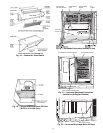
Route thermostat cable or equivalent single leads of colored
wire from thermostat subbase terminals to low-voltage connec-
tions on unit (shown in Fig. 10) as described in Steps 1-4
below.
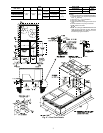
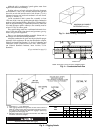
1. If unit is mounted on roof curb and accessory thru-the-
curb service plate connection is used, route wire through
connection plate.
2. Pass control wires through the hole provided on unit (see
connection D in Connection Sizes table in Fig. 6).
3. Feed wires through the raceway built into the corner post
to the 24-v barrier located on the left side of the control
box. See Fig. 11. The raceway provides the UL-required
(Underwriters’ Laboratories) clearance between high-
and low-voltage wiring.
4. Connect thermostat wires to screw terminals on low-
voltage connection board.
HEAT ANTICIPATOR SETTINGS — Set heat anticipator
settings at .14 amp for the first stage and .20 amp for second-
stage heating, except for 008 low heat. Set both first and sec-
ond stage heat anticipator settings for 008 at .14 amp.
Table 3 — American/European Wire Conversions
LEGEND
UNIT
48TF
NOMINAL
VOLTAGE
(50 Hz)
VOLTAGE
RANGE
COMPR
(ea)
OFM
(ea)
IFM POWER SUPPLY
MINIMUM UNIT
DISCONNECT
Min Max RLA LRA FLA FLA MCA MOCP* FLA LRA
008
400
(3 phase)
360 440 6.4 42.0 0.3 2.6 17.6 20 18 108
012
400
(3 phase)
360 440 8.9 52.0 0.3 2.6 23.2 30 24 128
014
400
(3 phase)
360 440 10.4 73.0 0.7 5.4 29.4 35 31 192
FLA —
Full Load Amps
HACR —
Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
IFM —
Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA —
Locked Rotor Amps
MCA —
Minimum Circuit Amps
MOCP —
Maximum Overcurrent Protection
NEC —
National Electrical Code (U.S.A.)
OFM —
Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA —
Rated Load Amps
= 100 x
max voltage deviation from average voltage
average voltage
Average Voltage =
393 + 403 + 396
3
=
1192
3
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is
more than 2%, contact your local electric utility company
immediately.
6
397
AMERICAN EUROPEAN
Industry
Standard Size
American
Conversion
Size (mm
2
)
Industry
Standard
Size (mm
2
)
18 AWG
0.82 1.0
16 AWG
1.30 1.5
14 AWG
2.08 2.5
12 AWG
3.30 4.0
10 AWG
5.25 6.0
8 AWG
6.36 10.0
6 AWG
13.29 16.0
4 AWG
21.14 25.0
3 AWG
26.65 —
2 AWG
33.61 35.0
1 AWG
42.39 50.0
1/0 AWG
53.49 —
2/0 AWG
67.42 70.0
3/0 AWG
85.00 95.0
4/0 AWG
107.19 120.0
250 kcmil
126.64 150.0
300 kcmil
151.97 —
350 kcmil
177.90 185.0
400 kcmil
202.63 240.0
500 kcmil
253.29 300.0
600 kcmil
303.95 —
AWG —
American Wire Gage
kcmil —
Thousand Circular Mils