Inlet Systems
Split/splitless capillary inlet
119
10 20 30 40 50 60
Area
Counts
+
1.2% Deviation
+
1.2% Deviation
~
20 ppm n-C
14
(Cold Trapped)
~
10 ppm n-C
11
(Solvent Effect)
Purge Activation Time, Sec
Solvent: Isooctane
Column: 16.5 m x 0.25 mm SE-54
80
C (0.5 min) 170 C@15 /min
Sample Size: 1.3 ml (Manual Injection)
Injection Rate: 1 ml/sec
Purge Flows: 5 ml/min, Septum: 60 ml/min, Inlet
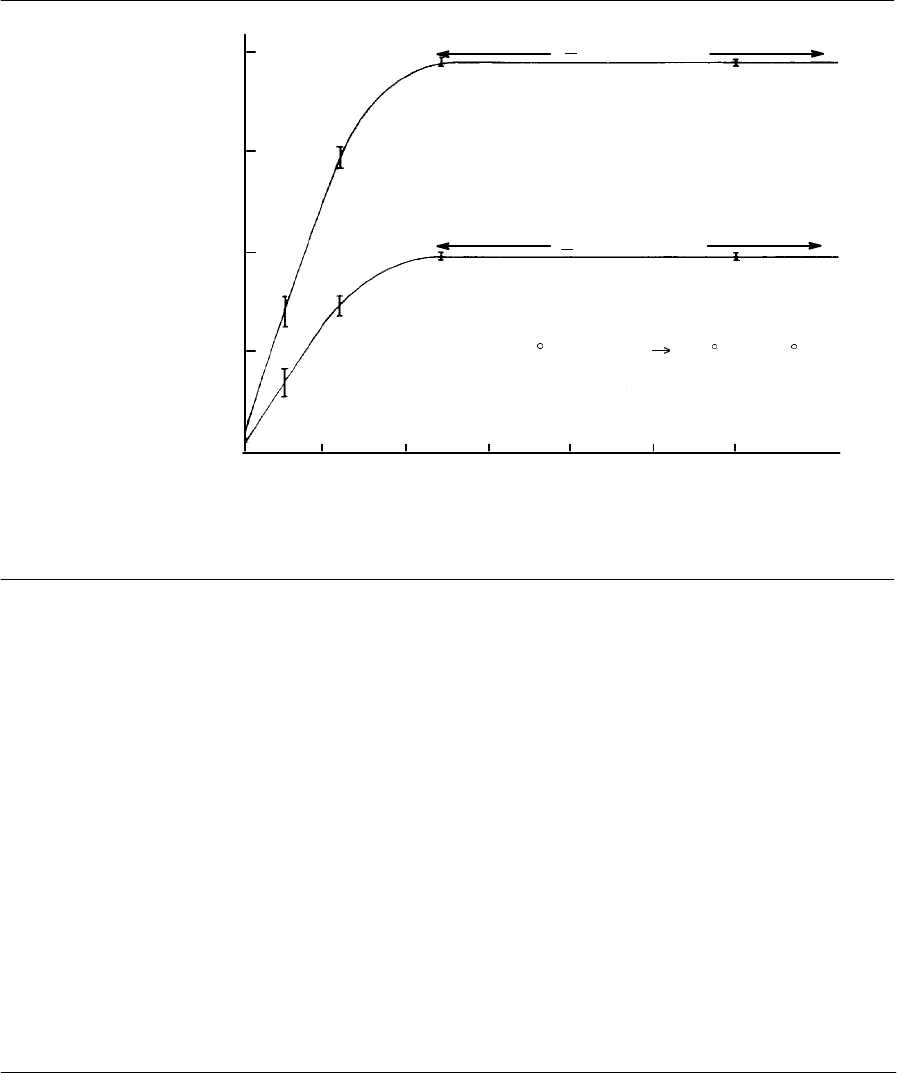
Effect of Inlet Purge Activation Time on Area Counts
Figure 6-10
Noting Figure 6•10,waiting too long does not increase component peak
areas, but does increase interference by the solvent tail. Purging too early
risks venting light components, not allowing sufficient time for heavier
components to enter the column, and/or not having sufficient solvent
enter the column to ensure good reconcentration.
A recommended procedure is to analyze a known standard using
conditions identical to those to be used for later sample analyses. Ideally,
the standard should be representative (in both components chosen and
their respective concentrations) of unknown samples to be analyzed.
Perform a series of analyses with increasingly delayed insert purge times:
the optimal time is where maximum area counts are obtained with least
interference by the solvent.
