13
CAUTION:
Do not use this product without a 3-amp fuse wired into the power
cable! Failure to use a 3-amp fuse will void your warranty.
This unit has reverse polarity protection. No damage will occur if the
power wires are reversed. However, the unit will not work until the
wires are attached correctly.
An optional 8-foot, CA-4 external power cable with a cigarette lighter
adapter is available from Lowrance.
NMEA/DGPS Cable Connections
NMEA is a standard communications format for marine electronic
equipment. For example, an autopilot can connect to the NMEA inter-
face on the GlobalMap 4000M and receive positioning information. The
GlobalMap 4000M can exchange information with any device that
transmits or receives NMEA 0183 data.
DGPS is an acronym for the Differential Global Positioning System.
DGPS supplements and boosts the accuracy of basic GPS. DGPS was
developed by the U.S. Coast Guard, which is responsible for the sys-
tem's operation in the United States. Since it's creation, DGPS has be-
come the international maritime standard for marine navigation.
The most popular DGPS system relies on a grid of ground-based trans-
mitters that send correction signals to DGPS receivers. These in turn,
connect to the GPS receiver (such as the GlobalMap 4000M). Lowrance
offers an optional DGPS receiver for your unit.
See the following diagrams for general wiring connections. Read your
other product’s owner’s manual for more wiring information.
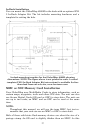
NMEA/DGPS Wiring
To exchange NMEA or DGPS data, the unit has two NMEA 0183 version
2.0 communication port. Com port one (Com-1) can be used to receive
NMEA format GPS data or DGPS data. Com-1 can also transmit NMEA
format GPS data to another device. Com-2 is for NMEA output only.
The three wires for the com port are combined with the two power
wires to form the power/data cable . Com-1 uses the yellow wire to
transmit, the orange wire to receive and the shield wire for signal
ground. Com-2 uses the blue wire for transmit.