7
Reference Manual
00809-0700-4530, Rev AA
Section 2: Installation Considerations
September 2013
Installation considerations
Apart from the additional cost of installation, there are some sizing and selection criteria for the
radar gauges that must be considered. This document outlines those considerations.
GWR is the preferred technology for shorter installations where rigid probes may be used. This
makes it a suitable replacement for caged displacers, which are often less than 10 ft. (3 m). The
probes are available in a variety of materials to handle corrosive fluids.
For further information on how to replace displacers with GWR in existing chambers, see the
Replacing Displacers with Guided Wave Radar Technical Note (Document No.
00840-2200-4811).
For taller applications or those with limited head space for installing rigid probes,
non-contacting radar may be advantageous. Non-contacting radar is also the preferred
technology for applications with heavy deposition or very sticky and viscous fluids.
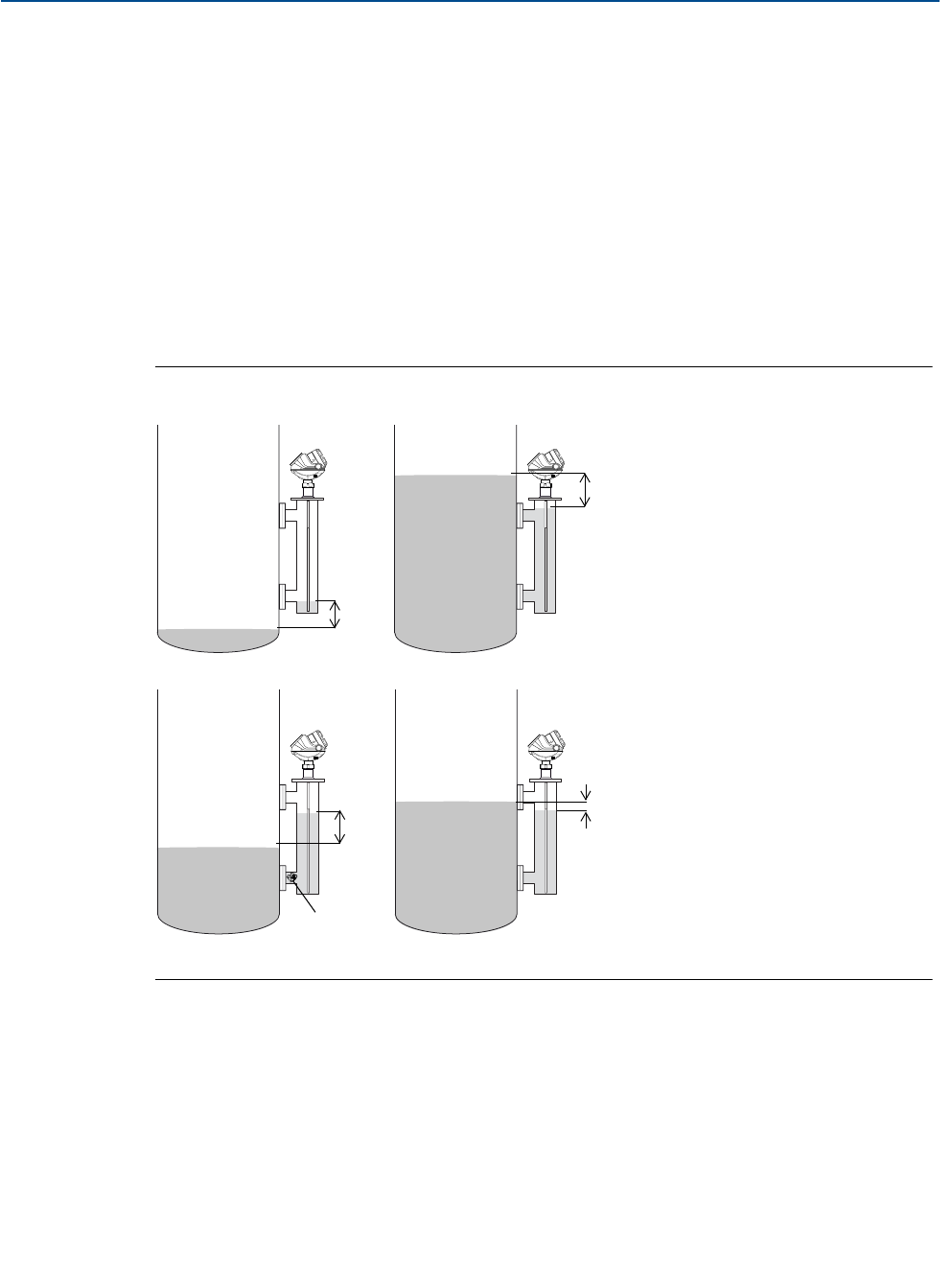
Figure 2-1. Possible error sources in chamber installations
For application guidelines, see Section 1: Power applications.
2.3.1 High pressure steam applications
Phase changes
It is especially common during startup to experience varying temperature and pressure. Both
the liquid and steam phases of the system will have density changes as the system reaches the
operating temperature and pressure which can cause up to a 30% error over temperature up to
600 °F (315 °C), as seen in Ta bl e 2- 1.
Error
Error
Error
Inlet-pipe
clogged
Error
300 °F (150 °C)
SG=0.80
150 °F (65 °C)
SG=0.85